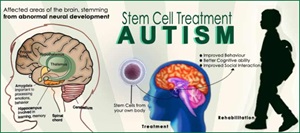
Duration of Treatment
10 Days
Days of Stay
2 Days in Hospital
Anesthesia
No need
Cost
8000 to 15000 USD
STEM CELL THERAPY FOR AUTISM COST IN INDIA
"Are you looking for the best hospital for stem cell therapy for autism cost in India? For more details, contact us via WhatsApp, Viber, or Telegram at +91 9582708782."
We have shortlisted the list of the best top Stem Cell Transplant Hospitals and Doctors based on Hospital accreditations, experience & qualification of doctors, success rates of procedures, and patient testimonials.
- Stem Cell Therapy For Autism Cost in India: from 8000 to 15000 USD.
- Hotel Cost Near Hospital - starting from 18 to 50 USD (as per hotel services)
- Food Cost - starting from 20 to 30 USD (per day)
- Miscellaneous cost - 20 USD (per day).
- It's only a rough estimate, final treatment will be planned after the fresh evaluation reports.
- Still, have questions? SUBMIT ENQUIRY
What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental condition that affects how a person communicates, behaves, learns, and interacts with others. It is referred to as a "spectrum" because individuals with autism exhibit a wide range of strengths, challenges, and abilities.
Key Features of Autism
-
Social Interaction Challenges:
- Difficulty understanding or responding to social cues (e.g., facial expressions, tone of voice).
- Challenges in forming and maintaining relationships.
- Preferring solitude or engaging in social interactions in unique ways.
-
Communication Differences:
- Delayed speech and language development in some individuals.
- Limited use of gestures, eye contact, or facial expressions to communicate.
- Difficulty understanding figurative language, sarcasm, or metaphors.
-
Repetitive Behaviors and Routines:
- Repetitive movements (e.g., hand-flapping, rocking).
- Strict adherence to routines and discomfort with change.
- Intense focus on specific topics or hobbies (referred to as "special interests").
-
Sensory Sensitivities:
- Heightened or diminished sensitivity to sensory input, such as sounds, lights, textures, or smells.
- Difficulty in environments that are noisy, crowded, or overstimulating.
Causes of Autism
The exact cause of autism is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Genetic Factors: Mutations or variations in certain genes have been linked to autism.
- Environmental Influences: Prenatal factors such as infections or exposure to toxins may play a role.
Note: Vaccines have been conclusively shown not to cause autism
Diagnosis
Autism is usually diagnosed in early childhood based on behavioral observations and developmental assessments. The diagnosis is made by specialists such as pediatricians, psychologists, or developmental neurologists.
- Common diagnostic tools include:
- DSM-5 Criteria (used by mental health professionals).
- Developmental screenings and behavioral evaluations.
Treatment and Support
While there is no "cure" for autism, various therapies and supports can help individuals manage challenges and build skills:
- Behavioral Therapy: Helps develop social, communication, and life skills.
- Speech Therapy: Improves language and communication abilities.
- Occupational Therapy: Supports sensory integration and daily activities.
- Educational Interventions: Tailored learning programs to address individual needs.
- Medication: May be prescribed to manage co-occurring conditions such as anxiety, ADHD, or irritability.
Strengths of Individuals with Autism
Many people with autism have unique strengths, including:
- Strong memory and attention to detail.
- Deep expertise in specific areas of interest.
- Creative thinking and problem-solving abilities.
Autism as Neurodiversity
Autism is increasingly viewed through the lens of neurodiversity, which emphasizes that differences in brain function are part of natural human diversity rather than deficits. People with autism contribute to society in unique and meaningful ways.
Best Hospital for Stem Cell Therapy for Autism in India
Best Centers for Stem Cell Therapy For Autism in India
Stem cell therapy for Autism in India is an emerging and experimental treatment for various conditions, including Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). While India has become a hub for advanced medical treatments, it's crucial to approach stem cell therapy for autism with caution due to the lack of conclusive evidence regarding its efficacy and safety. If you are considering this option, it's essential to choose reputable and accredited medical centers.
Reputable Stem Cell Therapy Centers in India
-
Regenerative Stem Cell Institute (RSCI)
- Location: Bangalore, Karnataka
- Overview: RSCI specializes in regenerative medicine and offers a range of stem cell therapies for various conditions. They focus on using mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from adipose tissue and bone marrow.
-
Advanced Stem Cell Technologies
- Location: Mumbai, Maharashtra
- Overview: This center offers stem cell treatments for neurological disorders, autoimmune diseases, and orthopedic conditions. They emphasize personalized treatment plans and advanced laboratory processing.
-
CureStem
- Location: Chennai, Tamil Nadu
- Overview: CureStem focuses on innovative stem cell therapies for a variety of conditions, including neurological and developmental disorders. They are involved in clinical research and trials.
-
Stempeutics Research
- Location: Bangalore, Karnataka
- Overview: Stempeutics is a leading biotechnology company specializing in stem cell research and therapy. They offer treatments for orthopedic, autoimmune, and other chronic conditions.
-
Vyome Biosciences
- Location: Mumbai, Maharashtra
- Overview: Vyome focuses on regenerative medicine and has developed proprietary stem cell technologies. They engage in clinical research and offer therapies for various medical conditions.
-
Stem Cell Care India
- Location: Mumbai, Maharashtra
- Overview: focuses on regenerative medicine and has developed proprietary stem cell technologies. They engage in clinical research and offer therapies for various medical conditions.
-
NeuroGen Brain and Spine Institute
- Location: Mumbai, Maharashtra
- Overview: Specializes in neurological disorders and provides stem cell therapy for autism, supported by scientific research.
-
Neurogen BSI
- Location: Mumbai, Maharashtra
- Overview: Specializes in neurological disorders and provides stem cell therapy for autism, supported by scientific research
-
Advancells
- Location: Noida, India
- Overview: Provides stem cell treatments for autism spectrum disorders, utilizing high-quality stem cells and Best Hospital for Stem Cell Therapy for Autism in India
-
Chaitanya Stem Cell Centre
- Location: Pune, India
- Overview: Offers stem cell therapy for autism, emphasizing advanced medical techniques and personalized care and Best Hospital for Stem Cell Therapy for Autism in India
Important Considerations:
-
Experimental Nature: Stem cell therapy for autism is still under research, and its efficacy and safety are not yet conclusively established.
-
Consultation: It's crucial to consult with qualified healthcare professionals to understand potential benefits and risks before considering such treatments.
-
Regulatory Status: Ensure that any treatment pursued complies with national medical guidelines and ethical standards.
-
Before making any decisions, thoroughly research each center, consult with medical experts, and consider all available treatment options.
Important Considerations
-
Clinical Evidence and Approval
- Experimental Nature: Stem cell therapy for autism is still in the experimental stages. There are limited clinical trials, and more research is needed to establish its safety and effectiveness.
- Regulatory Approval: Ensure that the treatment center adheres to guidelines set by the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) and the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR). Verify if the clinic has the necessary approvals for offering stem cell therapies. Best Hospital for Stem Cell Therapy for Autism in India
-
Clinic Credentials
- Accreditation: Choose centers that are accredited by recognized bodies such as the National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH).
- Qualified Professionals: Ensure that the medical team comprises qualified and experienced specialists in regenerative medicine and stem cell therapy and Best Hospital for Stem Cell Therapy for Autism in India
-
Safety and Ethical Standards
- Transparency: Reputable centers should provide clear information about the procedures, potential risks, and expected outcomes.
- Ethical Practices: Avoid clinics that make unverified claims or guarantee cures, as stem cell therapy for autism lacks definitive proof of efficacy.
-
Cost and Accessibility
- Cost Estimates: As previously mentioned, stem cell therapy costs in India can range from ₹3,30,000 to ₹8,00,000 per treatment cycle. Ensure you understand the pricing structure and what it includes.
- Follow-Up Care: Inquire about post-treatment support and follow-up services, which are crucial for monitoring progress and managing any adverse effects.
-
Consult Healthcare Professionals
- Medical Advice: Before pursuing stem cell therapy, consult with your child's healthcare provider or a specialist in autism. They can offer guidance on the most appropriate and evidence-based treatment options.
- Second Opinions: Consider seeking second opinions from multiple experts to make an informed decision.
Stem Cell Therapy Cost for Autism in India
Stem cell therapy for autism in India is an emerging treatment, with costs varying based on factors such as the medical facility, location, type of stem cells used, and the specific treatment protocol. Generally, the cost ranges from approximately $8,000 to USD 15,000 per treatment cycle.
Cost Breakdown
- Lower Range: Stem cell therapy for autism may start around $5,000 to $8,000 USD (approximately ₹3,65,000 to ₹5,84,000).
- Average Cost: Many estimates suggest an average cost starting from $12,000 USD (about ₹8,76,000).
- Higher Range: In some cases, costs can escalate up to $50,000 USD (approximately ₹36,50,000), depending on the complexity and specifics of the treatment.
Factors Influencing Cost
- Type of Stem Cells: The source and processing of stem cells (e.g., autologous vs. allogeneic) significantly impact the overall cost.
- Number of Treatment Cycles: Multiple treatment sessions may be required, increasing the total expenditure.
- Hospital Facilities and Location: Premium medical centers in metropolitan areas typically charge higher fees compared to those in other regions.
Key Considerations
While stem cell therapy for autism in India is available at costs ranging from approximately $8,000 to $15,000 USD per treatment cycle, it is important to approach this option with caution due to the lack of conclusive evidence regarding its efficacy and safety. Consulting a qualified medical professional and thoroughly understanding the potential risks and benefits is essential before proceeding with treatment.
What will be the Symptoms of stem cell therapy for Autism?
Stem cell therapy for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is an experimental treatment, and its symptoms or effects can vary widely depending on the individual, the type of stem cells used, and the treatment protocol.
It’s important to note that while some families report improvements in certain areas, there is no universal or guaranteed response to stem cell therapy.
Potential Positive Effects of Stem Cell Therapy for Autism
Some parents and caregivers have reported improvements in the following areas after stem cell therapy, though these are anecdotal and not universally observed:
1. Behavioral Improvements
- Reduced irritability or aggressive behaviors.
- Increased tolerance to changes in routine.
2. Social Interaction
- Improved eye contact and willingness to engage with others.
- Enhanced ability to recognize and respond to social cues.
3. Communication Skills
- Improved speech, vocabulary, or clarity in communication.
- Better understanding of verbal and non-verbal communication.
4. Cognitive Abilities
- Enhanced attention span or focus on tasks.
- Improved problem-solving or learning abilities.
5. Repetitive Behaviors
- Reduction in repetitive movements or restrictive patterns of behavior.
6. Sensory Sensitivities
- Decreased hypersensitivity or hyposensitivity to sensory stimuli, such as sounds, lights, or textures.
What will be the Side Effects of stem cell therapy for Autism?
Since stem cell therapy is still experimental, monitoring for potential side effects is crucial. Common side effects include:
1. Immediate Side Effects (Post-Treatment)
- Fever: A mild fever after treatment due to the body’s immune response.
- Fatigue: Temporary tiredness or lethargy.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Sometimes reported after administration.
2. Immune Reactions
- Inflammation: Localized or systemic inflammatory responses.
- Allergic Reactions: Reactions to stem cell products or administration materials.
3. Infections
- Risk of infection at the site of stem cell collection or administration (e.g., lumbar puncture or IV infusion).
4. Neurological Symptoms
- Headaches or dizziness, particularly if intrathecal (spinal) injections are used.
- Rare but possible neurological complications, such as seizures or worsening of symptoms.
5. Long-Term Risks
- Tumor Formation: Although rare, there is a theoretical risk of tumorigenesis if stem cells multiply uncontrollably.
- Unknown Long-Term Effects: Since the therapy is experimental, the long-term safety and efficacy are not well understood.
Factors Influencing the Outcome
The symptoms or effects of stem cell therapy can depend on:
- Type of Stem Cells: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) from bone marrow, adipose tissue, or umbilical cord blood are most commonly used.
- Delivery Method: Intravenous (IV) infusion, intrathecal injection, or other methods may yield different effects.
- Individual Differences: Age, severity of autism, and underlying health conditions can affect the response.
What will be the Preparation for stem cell therapy for Autism?
Preparation for stem cell therapy for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) involves several key steps to ensure the safety and efficacy of the treatment. As this therapy is experimental, working with a reputable medical center and experienced professionals is essential. Below are the typical steps for preparing for stem cell therapy:
1. Initial Assessment and Consultation
- Medical Evaluation: A thorough medical history review and physical examination will be conducted.
- Specialist Consultation: Meetings with developmental pediatricians, neurologists, or other specialists to assess the severity of autism symptoms and determine suitability for stem cell therapy.
- Behavioral and Developmental Assessments: Baseline tests to document current cognitive, communication, and social functioning levels.
2. Diagnostic Testing
- Blood Tests: To check overall health and rule out infections or underlying conditions.
- Imaging Studies (if needed): MRI or CT scans to evaluate neurological health.
- Genetic Testing: In some cases, genetic tests may be recommended to identify any chromosomal abnormalities or syndromes contributing to autism symptoms.
- Immune System Assessment: To ensure there are no contraindications related to immune response.
3. Preparation of Stem Cells
- Type of Stem Cells:
- Autologous (from the patient): May involve collecting stem cells from bone marrow, fat tissue, or peripheral blood.
- Allogeneic (from donors): Typically involves umbilical cord blood or other donor sources.
- Processing: The stem cells are processed in a lab to ensure they are safe and viable for therapeutic use.
4. Pre-Treatment Therapy
- Behavioral Therapy: Continuing speech, occupational, or ABA (Applied Behavior Analysis) therapy helps reinforce skills and monitor progress after treatment.
- Nutritional Support: A balanced diet and any prescribed supplements may be recommended to support overall health.
- Addressing Co-Occurring Conditions: Managing other conditions such as epilepsy, gastrointestinal issues, or anxiety that might interfere with treatment.
5. Informed Consent and Education
- Detailed Explanation: Understanding the experimental nature of the therapy, potential risks, benefits, and limitations.
- Consent Forms: Signing consent forms acknowledging awareness of the experimental status and possible outcomes.
- Counseling: Families may be offered counseling to manage expectations and address emotional or psychological concerns.
6. Travel and Logistics
- Location of Treatment: Many families travel to specialized centers; arrangements for travel and accommodation may be necessary.
- Duration of Stay: Depending on the treatment protocol, the stay could range from a few days to several weeks.
- Post-Treatment Plan: Ensure follow-up appointments are scheduled for monitoring and support.
7. Preparing the Patient
- Psychological Preparation: For children, explain the procedure in a way they can understand to minimize anxiety.
- Medications: Some medications may need to be adjusted or stopped before the procedure (e.g., blood thinners or immune-suppressing drugs).
- Avoiding Infections: Ensure the child avoids sick individuals and crowded areas to minimize the risk of infection before therapy.
8. Documentation
- Keep records of:
- Medical history and previous treatments.
- Developmental progress and therapies received.
- Any recent illnesses or hospitalizations.
- Family history of genetic or neurological conditions.
9. Financial Planning
- Cost of Therapy: Stem cell therapy is often expensive and not typically covered by insurance.
- Insurance Verification: Check whether any treatment components (diagnostic tests, consultations) are covered.
- Funding Options: Explore grants, fundraising, or other financial assistance if needed.
10. Post-Treatment Plan
- Arrange for continued therapies, such as behavioral and speech therapy, to maximize the potential benefits of stem cell therapy.
- Plan for regular follow-ups with the treatment center to monitor progress and address any side effects or complications.
What will be the Procedure for stem cell therapy for Autism?
Procedure for Stem Cell Therapy for Autism
The process of stem cell therapy for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) generally involves several steps, from patient evaluation to stem cell administration. Here’s a detailed overview of the procedure:
1. Pre-Treatment Phase
- Evaluation and Diagnosis:
- Comprehensive medical and psychological assessments to confirm the diagnosis and determine suitability for therapy.
- Tests and Screening:
- Blood tests, imaging (MRI/CT), immune system evaluation, and possibly genetic testing.
- Stem Cell Selection:
- Based on the source, stem cells may be:
- Autologous (harvested from the patient’s own body, such as bone marrow or adipose tissue).
- Allogeneic (donor-derived, such as umbilical cord blood or other sources).
- Based on the source, stem cells may be:
- Informed Consent:
- Detailed discussions about the therapy, risks, and potential outcomes, followed by signing consent forms.
2. Harvesting Stem Cells (if Autologous)
- Bone Marrow Aspiration:
- Performed under local or general anesthesia.
- A needle is used to extract bone marrow, usually from the pelvic bone.
- Adipose Tissue Extraction:
- A small amount of fat is removed, typically from the abdomen, using a minimally invasive liposuction procedure.
- Peripheral Blood Collection (if applicable):
- Blood is drawn, and stem cells are separated using apheresis.
3. Processing and Preparation
- Isolation and Culturing:
- Stem cells are processed in a laboratory to ensure purity and viability.
- Quality Control:
- The cells are tested for contamination and prepared for administration.
4. Administration of Stem Cells
The method of delivering stem cells varies based on the treatment protocol and medical center:
Intravenous (IV) Infusion:
- The most common and minimally invasive method.
- Stem cells are infused directly into a vein, allowing them to travel through the bloodstream and potentially target areas of inflammation or dysfunction.
Intrathecal (Spinal) Injection:
- Stem cells are injected into the cerebrospinal fluid via a lumbar puncture.
- This method aims to directly deliver stem cells closer to the brain and nervous system.
- Performed under local or general anesthesia to minimize discomfort.
Intranasal Administration (Less Common):
- Stem cells are delivered via the nasal cavity, allowing them to bypass the blood-brain barrier and reach the central nervous system.
5. Post-Treatment Observation
- Immediate Monitoring:
- The patient is observed for a few hours or overnight for any adverse reactions, such as fever, nausea, or allergic responses.
- Discharge Instructions:
- Patients are advised on activity restrictions and follow-up care.
6. Follow-Up and Rehabilitation
- Therapeutic Support:
- Continuation of behavioral therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy to enhance potential benefits.
- Progress Monitoring:
- Regular follow-ups with the medical team to evaluate improvements in symptoms and address any complications.
- Additional Cycles (if needed):
- Some protocols may recommend multiple stem cell therapy sessions spaced over weeks or months.
Expected Duration
- The entire process, from harvesting to administration, may take several days to weeks, depending on the type of stem cells used and the protocol.
Risks and Safety
- Potential Side Effects:
- Fever, fatigue, or local pain at the injection site.
- Rare but serious risks include infection, immune reactions, or neurological complications.
- Experimental Nature:
- Stem cell therapy for autism is not yet conclusively proven, and outcomes can vary.
Key Considerations
- Ensure the therapy is conducted at an accredited and reputable medical center.
- Be realistic about outcomes, as the efficacy of stem cell therapy for autism is still being researched.
- Regular therapies, such as behavioral and speech therapy, remain crucial alongside stem cell treatment.
If you are considering stem cell therapy, consult with specialists to determine if this treatment is appropriate for your child’s specific needs
What will be the Post-Care for stem cell therapy for Autism?
Post-Care for Stem Cell Therapy in Autism
Post-care after stem cell therapy for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a critical part of the treatment process. It ensures the safety of the patient, helps monitor progress, and optimizes potential benefits. Here's what the post-treatment care typically involves:
1. Immediate Post-Treatment Care
- Observation Period:
- After the procedure, the patient is observed for a few hours to ensure there are no immediate adverse reactions, such as fever, nausea, or pain.
- Pain Management:
- If bone marrow or adipose tissue was harvested, mild pain or discomfort at the extraction site might occur. Over-the-counter pain relievers may be recommended.
- Rest:
- The patient may need rest for 1–2 days, depending on the method of administration (e.g., intravenous or intrathecal).
2. Monitor for Side Effects
- Common Side Effects:
- Mild fever, fatigue, headache, or local pain at the injection or harvesting site.
- Serious Reactions:
- Rare but possible issues include infection, allergic reactions, or neurological symptoms (especially with intrathecal injections). Contact your doctor immediately if these occur.
- Follow-Up Appointments:
- Schedule regular follow-ups to monitor for any delayed side effects or complications.
3. Supportive Therapies
- Behavioral Therapy:
- Continue or start Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), cognitive behavioral therapy, or similar interventions to reinforce social, communication, and behavioral skills.
- Speech Therapy:
- Helps improve verbal and non-verbal communication, building on any progress from the stem cell therapy.
- Occupational Therapy:
- Focuses on sensory integration, motor skills, and daily living skills.
- Educational Support:
- Work with educators to tailor learning strategies to the child’s evolving needs.
4. Lifestyle Adjustments
- Diet and Nutrition:
- A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports overall health and recovery. Some clinicians may recommend supplements (e.g., omega-3 fatty acids) if beneficial.
- Hydration:
- Encourage adequate fluid intake to support cellular health and recovery.
- Physical Activity:
- Light physical activities may be encouraged, but strenuous activities should be avoided for a few days, especially after intrathecal injections or harvesting procedures.
5. Emotional and Psychological Support
- Counseling:
- Parents and caregivers may benefit from counseling or support groups to manage expectations and emotional challenges.
- Social Skills Groups:
- Enroll the child in programs that help with interaction and communication in structured group settings.
6. Progress Tracking
- Document Changes:
- Maintain a journal to record behavioral, communication, and social changes post-treatment. This helps monitor progress and share observations with healthcare providers.
- Regular Assessments:
- Repeat developmental and behavioral evaluations at intervals (e.g., 3 months, 6 months, and 12 months post-therapy) to assess improvements and plan additional interventions.
7. Long-Term Care
- Additional Cycles:
- Some treatment protocols recommend additional stem cell therapy sessions over months or years. Your doctor will advise based on progress and medical assessments.
- Multidisciplinary Approach:
- Work with a team of specialists, including pediatricians, neurologists, and therapists, for holistic care.
8. Addressing Expectations
- Realistic Outcomes:
- Improvements may take weeks to months to manifest, and results vary widely among individuals. Some children may show noticeable changes in communication, behavior, or sensory responses, while others may have minimal or no changes.
- Patience and Persistence:
- Combine stem cell therapy with consistent therapeutic interventions to maximize the potential for positive outcomes.
When to Seek Medical Help
Contact your healthcare provider immediately if the patient experiences:
- Persistent fever or fatigue.
- Severe headaches, dizziness, or seizures.
- Signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge at the injection or harvesting site.
- Unusual changes in behavior or neurological symptoms.
Key Takeaways
- Post-care is essential to ensure the safety and success of stem cell therapy.
- Regular therapies like behavioral, speech, and occupational therapy remain critical for sustained progress.
- Monitor the patient closely for any side effects and keep communication open with the medical team.
- Manage expectations and focus on long-term, holistic support for the patient.
By maintaining a structured and supportive post-care plan, you can help maximize the potential benefits of stem cell therapy for autism.
What will be the Success Rate for stem cell therapy for Autism?
Success Rate for Stem Cell Therapy in Autism
The success rate of stem cell therapy for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is currently not well-established due to its experimental nature and the lack of large-scale, long-term clinical trials. Outcomes vary widely among individuals, and the treatment is not universally effective. Here's an overview of what is known about the potential success and limitations:
Factors Influencing Success
-
Severity of Autism:
- Children with milder symptoms may show more noticeable improvements in social interaction, communication, or behavior.
-
Type of Stem Cells Used:
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) from sources like bone marrow, adipose tissue, or umbilical cord blood are the most commonly studied. These cells are believed to have anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties that may help improve neurological function.
-
Delivery Method:
- Intravenous (IV) or intrathecal (spinal) administration may influence the treatment's efficacy. Intrathecal delivery is thought to target the central nervous system more directly.
-
Age of the Patient:
- Younger children may respond better, as their brains are still developing and might be more receptive to regenerative treatments.
-
Complementary Therapies:
- The combination of stem cell therapy with behavioral, speech, or occupational therapies often yields better outcomes.
-
Underlying Medical Issues:
- Children with co-existing conditions, such as epilepsy or severe immune dysfunction, may have variable responses to treatment.
Reported Improvements
While scientific evidence is limited, anecdotal reports and small studies have documented some improvements in the following areas:
- Social Interaction: Increased eye contact, better social engagement, and improved response to social cues.
- Communication Skills: Enhanced verbal abilities, increased vocabulary, and improved clarity of speech.
- Behavioral Symptoms: Reduced hyperactivity, aggression, and irritability.
- Cognitive Abilities: Improved focus, problem-solving, and learning capacity.
- Sensory Sensitivities: Better tolerance to sensory stimuli, such as sounds, lights, and textures.
Limitations and Concerns
-
Lack of Standardization:
- Different clinics use varying protocols, making it difficult to compare outcomes or establish a definitive success rate.
-
Small-Scale Studies:
- Most studies have been conducted on small groups, with limited follow-up periods. Results are often anecdotal and not peer-reviewed.
-
Unpredictable Results:
- Some individuals show noticeable improvements, while others experience minimal or no changes.
-
Placebo Effect:
- In some cases, perceived improvements may be due to the placebo effect or increased attention to therapies post-treatment.
-
Risks and Ethical Concerns:
- The experimental nature of the therapy raises concerns about safety, especially in clinics without proper regulatory oversight.
Current Research Findings
- A few studies have reported improvements in behavioral symptoms and quality of life, but these results are preliminary and not conclusive.
- Clinical trials are ongoing worldwide to better understand the potential of stem cell therapy for autism, including its mechanisms, safety, and efficacy.
Estimated Success Rates
While exact success rates are not available, anecdotal reports and small studies suggest:
- Mild to Moderate Autism: Approximately 40–60% of children may show some improvement in symptoms, but the degree of improvement varies.
- Severe Autism: Lower success rates are reported, with improvements generally focused on reducing irritability or aggression rather than enhancing communication or social skills.
Realistic Expectations
- Not a Cure: Stem cell therapy is not a cure for autism. At best, it may alleviate certain symptoms or improve quality of life.
- Complementary Treatment: It should be viewed as part of a broader, multidisciplinary approach, including traditional therapies.
- Gradual Changes: Improvements, if they occur, may take weeks to months to become noticeable.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy for autism is still in the experimental stage, and its success cannot be guaranteed. Families considering this treatment should:
- Consult with reputable medical professionals.
- Choose accredited centers that follow ethical and scientific guidelines.
- Combine the therapy with evidence-based treatments for the best outcomes.
- Monitor the child’s progress and maintain realistic expectations about the results.
Continuing advancements in research may provide clearer insights into the success rates and mechanisms of stem cell therapy for autism in the future.
FAQs for Stem Cell Therapy for Autism in India
Here’s a comprehensive list of frequently asked questions (FAQs) about stem cell therapy for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in India:
General Questions
1. What is stem cell therapy for autism?
Stem cell therapy is an experimental treatment that involves using stem cells to repair, regenerate, or modulate dysfunctional neural pathways associated with autism. The therapy aims to reduce inflammation in the brain and promote neural development.
2. Is stem cell therapy for autism approved in India?
Stem cell therapy for autism is classified as experimental in India. It is not yet approved as a standard treatment but is allowed under specific clinical research guidelines overseen by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO).
3. Who is eligible for stem cell therapy for autism?
Eligibility is determined after a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, developmental progress, and behavioral symptoms. Typically, individuals with ASD showing significant deficits in social, communication, or behavioral skills may be considered.
Procedure-Related Questions
4. How are stem cells administered?
Stem cells are administered via:
- Intravenous (IV) infusion: Through a vein.
- Intrathecal injection: Into the cerebrospinal fluid via the spine.
- Intranasal delivery: (Less common) through the nasal cavity.
5. What types of stem cells are used for autism therapy?
- Autologous stem cells: Derived from the patient’s own body (e.g., bone marrow or adipose tissue).
- Allogeneic stem cells: Donor-derived cells, such as umbilical cord blood stem cells.
6. How long does the procedure take?
The duration depends on the method of administration:
- Stem Cell Harvesting: 1–2 hours (if autologous).
- Processing and Administration: 1–3 days.
7. Is stem cell therapy painful?
Most procedures, such as IV infusion, are minimally invasive and painless. If harvesting is required (e.g., bone marrow aspiration), mild discomfort may occur but is usually managed with local or general anesthesia.
Cost and Availability
8. How much does stem cell therapy for autism cost in India?
The cost ranges from 8000 to 15000 USD or more, depending on:
- The type and source of stem cells used.
- The treatment center and its location.
- The number of therapy cycles recommended.
9. Are there specialized centers for stem cell therapy for autism in India?
Yes, some reputed centers include:
- NeuroGen Brain and Spine Institute, Mumbai.
- Advancells, Noida.
- StemRx Bioscience Solutions, Navi Mumbai.
- Nutech Mediworld, Delhi.
10. Is stem cell therapy covered by insurance in India?
No, stem cell therapy for autism is not covered by insurance in India because it is still considered experimental.
Effectiveness and Safety
11. Is stem cell therapy a cure for autism?
No, stem cell therapy is not a cure for autism. It is aimed at improving specific symptoms, such as communication, social interaction, and behavior.
12. What are the success rates for stem cell therapy in autism?
The success rate is variable. Some studies report improvements in 40–60% of cases for mild to moderate autism, but outcomes differ widely. Long-term efficacy is still under research.
13. Are there risks or side effects?
Common side effects include:
- Mild fever.
- Local pain at the injection site.
- Rare risks include infection, immune reactions, or neurological complications.
Post-Treatment Care
14. What is the recovery time after therapy?
Most patients resume normal activities within a day or two after the procedure. Full recovery from any harvesting process (if applicable) may take up to a week.
15. How long does it take to see results?
Results may take several weeks to months, and the degree of improvement varies. Some children show changes in behavior, communication, or sensory responses over 6–12 months.
Regulations and Ethics
16. Is stem cell therapy for autism ethical?
The treatment is considered ethical if conducted under approved clinical trials or research protocols. Families should ensure they are working with accredited and licensed medical centers.
17. How can I verify the credibility of a treatment center in India?
- Check if the center is accredited by the National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH).
- Confirm adherence to ICMR and CDSCO guidelines.
- Review patient testimonials and published clinical trial data (if available).
Decision-Making
18. Should I try stem cell therapy for my child with autism?
This decision depends on:
- The severity of your child’s symptoms.
- Consultation with medical professionals.
- Understanding the experimental nature, costs, and potential risks of the therapy.
19. What should I do if I’m interested in stem cell therapy for autism?
- Consult a developmental pediatrician or neurologist.
- Contact reputable stem cell therapy centers for detailed evaluations.
- Research the treatment protocols, costs, and expected outcomes.
20. Are there alternatives to stem cell therapy?
Yes, evidence-based alternatives include:
- Behavioral Therapies: Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), speech therapy, and occupational therapy.
- Medications: For managing specific symptoms like hyperactivity or anxiety.
- Nutritional Support: Diet modifications and supplements.
Final Note
Stem cell therapy for autism in India is a promising but experimental approach. Families should consult trusted medical experts and carefully evaluate the potential benefits and risks before proceeding.
Top Doctors
Sorry, There is nothing to show!Come back soon.
Top Hospitals
STEM CELL THERAPY FOR AUTISM COST IN INDIA

Duration of Treatment
10 Days
Days of Stay
2 Days in Hospital
Anesthesia
No need
Cost
8000 to 15000 USD
STEM CELL THERAPY FOR AUTISM COST IN INDIA
"Are you looking for the best hospital for stem cell therapy for autism cost in India? For more details, contact us via WhatsApp, Viber, or Telegram at +91 9582708782."
We have shortlisted the list of the best top Stem Cell Transplant Hospitals and Doctors based on Hospital accreditations, experience & qualification of doctors, success rates of procedures, and patient testimonials.
- Stem Cell Therapy For Autism Cost in India: from 8000 to 15000 USD.
- Hotel Cost Near Hospital - starting from 18 to 50 USD (as per hotel services)
- Food Cost - starting from 20 to 30 USD (per day)
- Miscellaneous cost - 20 USD (per day).
- It's only a rough estimate, final treatment will be planned after the fresh evaluation reports.
- Still, have questions? SUBMIT ENQUIRY
What Is Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)?
Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a developmental condition that affects how a person communicates, behaves, learns, and interacts with others. It is referred to as a "spectrum" because individuals with autism exhibit a wide range of strengths, challenges, and abilities.
Key Features of Autism
-
Social Interaction Challenges:
- Difficulty understanding or responding to social cues (e.g., facial expressions, tone of voice).
- Challenges in forming and maintaining relationships.
- Preferring solitude or engaging in social interactions in unique ways.
-
Communication Differences:
- Delayed speech and language development in some individuals.
- Limited use of gestures, eye contact, or facial expressions to communicate.
- Difficulty understanding figurative language, sarcasm, or metaphors.
-
Repetitive Behaviors and Routines:
- Repetitive movements (e.g., hand-flapping, rocking).
- Strict adherence to routines and discomfort with change.
- Intense focus on specific topics or hobbies (referred to as "special interests").
-
Sensory Sensitivities:
- Heightened or diminished sensitivity to sensory input, such as sounds, lights, textures, or smells.
- Difficulty in environments that are noisy, crowded, or overstimulating.
Causes of Autism
The exact cause of autism is not fully understood, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Genetic Factors: Mutations or variations in certain genes have been linked to autism.
- Environmental Influences: Prenatal factors such as infections or exposure to toxins may play a role.
Note: Vaccines have been conclusively shown not to cause autism
Diagnosis
Autism is usually diagnosed in early childhood based on behavioral observations and developmental assessments. The diagnosis is made by specialists such as pediatricians, psychologists, or developmental neurologists.
- Common diagnostic tools include:
- DSM-5 Criteria (used by mental health professionals).
- Developmental screenings and behavioral evaluations.
Treatment and Support
While there is no "cure" for autism, various therapies and supports can help individuals manage challenges and build skills:
- Behavioral Therapy: Helps develop social, communication, and life skills.
- Speech Therapy: Improves language and communication abilities.
- Occupational Therapy: Supports sensory integration and daily activities.
- Educational Interventions: Tailored learning programs to address individual needs.
- Medication: May be prescribed to manage co-occurring conditions such as anxiety, ADHD, or irritability.
Strengths of Individuals with Autism
Many people with autism have unique strengths, including:
- Strong memory and attention to detail.
- Deep expertise in specific areas of interest.
- Creative thinking and problem-solving abilities.
Autism as Neurodiversity
Autism is increasingly viewed through the lens of neurodiversity, which emphasizes that differences in brain function are part of natural human diversity rather than deficits. People with autism contribute to society in unique and meaningful ways.
Best Hospital for Stem Cell Therapy for Autism in India
Best Centers for Stem Cell Therapy For Autism in India
Stem cell therapy for Autism in India is an emerging and experimental treatment for various conditions, including Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD). While India has become a hub for advanced medical treatments, it's crucial to approach stem cell therapy for autism with caution due to the lack of conclusive evidence regarding its efficacy and safety. If you are considering this option, it's essential to choose reputable and accredited medical centers.
Reputable Stem Cell Therapy Centers in India
-
Regenerative Stem Cell Institute (RSCI)
- Location: Bangalore, Karnataka
- Overview: RSCI specializes in regenerative medicine and offers a range of stem cell therapies for various conditions. They focus on using mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) derived from adipose tissue and bone marrow.
-
Advanced Stem Cell Technologies
- Location: Mumbai, Maharashtra
- Overview: This center offers stem cell treatments for neurological disorders, autoimmune diseases, and orthopedic conditions. They emphasize personalized treatment plans and advanced laboratory processing.
-
CureStem
- Location: Chennai, Tamil Nadu
- Overview: CureStem focuses on innovative stem cell therapies for a variety of conditions, including neurological and developmental disorders. They are involved in clinical research and trials.
-
Stempeutics Research
- Location: Bangalore, Karnataka
- Overview: Stempeutics is a leading biotechnology company specializing in stem cell research and therapy. They offer treatments for orthopedic, autoimmune, and other chronic conditions.
-
Vyome Biosciences
- Location: Mumbai, Maharashtra
- Overview: Vyome focuses on regenerative medicine and has developed proprietary stem cell technologies. They engage in clinical research and offer therapies for various medical conditions.
-
Stem Cell Care India
- Location: Mumbai, Maharashtra
- Overview: focuses on regenerative medicine and has developed proprietary stem cell technologies. They engage in clinical research and offer therapies for various medical conditions.
-
NeuroGen Brain and Spine Institute
- Location: Mumbai, Maharashtra
- Overview: Specializes in neurological disorders and provides stem cell therapy for autism, supported by scientific research.
-
Neurogen BSI
- Location: Mumbai, Maharashtra
- Overview: Specializes in neurological disorders and provides stem cell therapy for autism, supported by scientific research
-
Advancells
- Location: Noida, India
- Overview: Provides stem cell treatments for autism spectrum disorders, utilizing high-quality stem cells and Best Hospital for Stem Cell Therapy for Autism in India
-
Chaitanya Stem Cell Centre
- Location: Pune, India
- Overview: Offers stem cell therapy for autism, emphasizing advanced medical techniques and personalized care and Best Hospital for Stem Cell Therapy for Autism in India
Important Considerations:
-
Experimental Nature: Stem cell therapy for autism is still under research, and its efficacy and safety are not yet conclusively established.
-
Consultation: It's crucial to consult with qualified healthcare professionals to understand potential benefits and risks before considering such treatments.
-
Regulatory Status: Ensure that any treatment pursued complies with national medical guidelines and ethical standards.
-
Before making any decisions, thoroughly research each center, consult with medical experts, and consider all available treatment options.
Important Considerations
-
Clinical Evidence and Approval
- Experimental Nature: Stem cell therapy for autism is still in the experimental stages. There are limited clinical trials, and more research is needed to establish its safety and effectiveness.
- Regulatory Approval: Ensure that the treatment center adheres to guidelines set by the Drug Controller General of India (DCGI) and the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR). Verify if the clinic has the necessary approvals for offering stem cell therapies. Best Hospital for Stem Cell Therapy for Autism in India
-
Clinic Credentials
- Accreditation: Choose centers that are accredited by recognized bodies such as the National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH).
- Qualified Professionals: Ensure that the medical team comprises qualified and experienced specialists in regenerative medicine and stem cell therapy and Best Hospital for Stem Cell Therapy for Autism in India
-
Safety and Ethical Standards
- Transparency: Reputable centers should provide clear information about the procedures, potential risks, and expected outcomes.
- Ethical Practices: Avoid clinics that make unverified claims or guarantee cures, as stem cell therapy for autism lacks definitive proof of efficacy.
-
Cost and Accessibility
- Cost Estimates: As previously mentioned, stem cell therapy costs in India can range from ₹3,30,000 to ₹8,00,000 per treatment cycle. Ensure you understand the pricing structure and what it includes.
- Follow-Up Care: Inquire about post-treatment support and follow-up services, which are crucial for monitoring progress and managing any adverse effects.
-
Consult Healthcare Professionals
- Medical Advice: Before pursuing stem cell therapy, consult with your child's healthcare provider or a specialist in autism. They can offer guidance on the most appropriate and evidence-based treatment options.
- Second Opinions: Consider seeking second opinions from multiple experts to make an informed decision.
Stem Cell Therapy Cost for Autism in India
Stem cell therapy for autism in India is an emerging treatment, with costs varying based on factors such as the medical facility, location, type of stem cells used, and the specific treatment protocol. Generally, the cost ranges from approximately $8,000 to USD 15,000 per treatment cycle.
Cost Breakdown
- Lower Range: Stem cell therapy for autism may start around $5,000 to $8,000 USD (approximately ₹3,65,000 to ₹5,84,000).
- Average Cost: Many estimates suggest an average cost starting from $12,000 USD (about ₹8,76,000).
- Higher Range: In some cases, costs can escalate up to $50,000 USD (approximately ₹36,50,000), depending on the complexity and specifics of the treatment.
Factors Influencing Cost
- Type of Stem Cells: The source and processing of stem cells (e.g., autologous vs. allogeneic) significantly impact the overall cost.
- Number of Treatment Cycles: Multiple treatment sessions may be required, increasing the total expenditure.
- Hospital Facilities and Location: Premium medical centers in metropolitan areas typically charge higher fees compared to those in other regions.
Key Considerations
While stem cell therapy for autism in India is available at costs ranging from approximately $8,000 to $15,000 USD per treatment cycle, it is important to approach this option with caution due to the lack of conclusive evidence regarding its efficacy and safety. Consulting a qualified medical professional and thoroughly understanding the potential risks and benefits is essential before proceeding with treatment.
symptoms
What will be the Symptoms of stem cell therapy for Autism?
Stem cell therapy for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is an experimental treatment, and its symptoms or effects can vary widely depending on the individual, the type of stem cells used, and the treatment protocol.
It’s important to note that while some families report improvements in certain areas, there is no universal or guaranteed response to stem cell therapy.
Potential Positive Effects of Stem Cell Therapy for Autism
Some parents and caregivers have reported improvements in the following areas after stem cell therapy, though these are anecdotal and not universally observed:
1. Behavioral Improvements
- Reduced irritability or aggressive behaviors.
- Increased tolerance to changes in routine.
2. Social Interaction
- Improved eye contact and willingness to engage with others.
- Enhanced ability to recognize and respond to social cues.
3. Communication Skills
- Improved speech, vocabulary, or clarity in communication.
- Better understanding of verbal and non-verbal communication.
4. Cognitive Abilities
- Enhanced attention span or focus on tasks.
- Improved problem-solving or learning abilities.
5. Repetitive Behaviors
- Reduction in repetitive movements or restrictive patterns of behavior.
6. Sensory Sensitivities
- Decreased hypersensitivity or hyposensitivity to sensory stimuli, such as sounds, lights, or textures.
risk factors
What will be the Side Effects of stem cell therapy for Autism?
Since stem cell therapy is still experimental, monitoring for potential side effects is crucial. Common side effects include:
1. Immediate Side Effects (Post-Treatment)
- Fever: A mild fever after treatment due to the body’s immune response.
- Fatigue: Temporary tiredness or lethargy.
- Nausea or Vomiting: Sometimes reported after administration.
2. Immune Reactions
- Inflammation: Localized or systemic inflammatory responses.
- Allergic Reactions: Reactions to stem cell products or administration materials.
3. Infections
- Risk of infection at the site of stem cell collection or administration (e.g., lumbar puncture or IV infusion).
4. Neurological Symptoms
- Headaches or dizziness, particularly if intrathecal (spinal) injections are used.
- Rare but possible neurological complications, such as seizures or worsening of symptoms.
5. Long-Term Risks
- Tumor Formation: Although rare, there is a theoretical risk of tumorigenesis if stem cells multiply uncontrollably.
- Unknown Long-Term Effects: Since the therapy is experimental, the long-term safety and efficacy are not well understood.
Factors Influencing the Outcome
The symptoms or effects of stem cell therapy can depend on:
- Type of Stem Cells: Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) from bone marrow, adipose tissue, or umbilical cord blood are most commonly used.
- Delivery Method: Intravenous (IV) infusion, intrathecal injection, or other methods may yield different effects.
- Individual Differences: Age, severity of autism, and underlying health conditions can affect the response.
preparation
What will be the Preparation for stem cell therapy for Autism?
Preparation for stem cell therapy for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) involves several key steps to ensure the safety and efficacy of the treatment. As this therapy is experimental, working with a reputable medical center and experienced professionals is essential. Below are the typical steps for preparing for stem cell therapy:
1. Initial Assessment and Consultation
- Medical Evaluation: A thorough medical history review and physical examination will be conducted.
- Specialist Consultation: Meetings with developmental pediatricians, neurologists, or other specialists to assess the severity of autism symptoms and determine suitability for stem cell therapy.
- Behavioral and Developmental Assessments: Baseline tests to document current cognitive, communication, and social functioning levels.
2. Diagnostic Testing
- Blood Tests: To check overall health and rule out infections or underlying conditions.
- Imaging Studies (if needed): MRI or CT scans to evaluate neurological health.
- Genetic Testing: In some cases, genetic tests may be recommended to identify any chromosomal abnormalities or syndromes contributing to autism symptoms.
- Immune System Assessment: To ensure there are no contraindications related to immune response.
3. Preparation of Stem Cells
- Type of Stem Cells:
- Autologous (from the patient): May involve collecting stem cells from bone marrow, fat tissue, or peripheral blood.
- Allogeneic (from donors): Typically involves umbilical cord blood or other donor sources.
- Processing: The stem cells are processed in a lab to ensure they are safe and viable for therapeutic use.
4. Pre-Treatment Therapy
- Behavioral Therapy: Continuing speech, occupational, or ABA (Applied Behavior Analysis) therapy helps reinforce skills and monitor progress after treatment.
- Nutritional Support: A balanced diet and any prescribed supplements may be recommended to support overall health.
- Addressing Co-Occurring Conditions: Managing other conditions such as epilepsy, gastrointestinal issues, or anxiety that might interfere with treatment.
5. Informed Consent and Education
- Detailed Explanation: Understanding the experimental nature of the therapy, potential risks, benefits, and limitations.
- Consent Forms: Signing consent forms acknowledging awareness of the experimental status and possible outcomes.
- Counseling: Families may be offered counseling to manage expectations and address emotional or psychological concerns.
6. Travel and Logistics
- Location of Treatment: Many families travel to specialized centers; arrangements for travel and accommodation may be necessary.
- Duration of Stay: Depending on the treatment protocol, the stay could range from a few days to several weeks.
- Post-Treatment Plan: Ensure follow-up appointments are scheduled for monitoring and support.
7. Preparing the Patient
- Psychological Preparation: For children, explain the procedure in a way they can understand to minimize anxiety.
- Medications: Some medications may need to be adjusted or stopped before the procedure (e.g., blood thinners or immune-suppressing drugs).
- Avoiding Infections: Ensure the child avoids sick individuals and crowded areas to minimize the risk of infection before therapy.
8. Documentation
- Keep records of:
- Medical history and previous treatments.
- Developmental progress and therapies received.
- Any recent illnesses or hospitalizations.
- Family history of genetic or neurological conditions.
9. Financial Planning
- Cost of Therapy: Stem cell therapy is often expensive and not typically covered by insurance.
- Insurance Verification: Check whether any treatment components (diagnostic tests, consultations) are covered.
- Funding Options: Explore grants, fundraising, or other financial assistance if needed.
10. Post-Treatment Plan
- Arrange for continued therapies, such as behavioral and speech therapy, to maximize the potential benefits of stem cell therapy.
- Plan for regular follow-ups with the treatment center to monitor progress and address any side effects or complications.
procedure
What will be the Procedure for stem cell therapy for Autism?
Procedure for Stem Cell Therapy for Autism
The process of stem cell therapy for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) generally involves several steps, from patient evaluation to stem cell administration. Here’s a detailed overview of the procedure:
1. Pre-Treatment Phase
- Evaluation and Diagnosis:
- Comprehensive medical and psychological assessments to confirm the diagnosis and determine suitability for therapy.
- Tests and Screening:
- Blood tests, imaging (MRI/CT), immune system evaluation, and possibly genetic testing.
- Stem Cell Selection:
- Based on the source, stem cells may be:
- Autologous (harvested from the patient’s own body, such as bone marrow or adipose tissue).
- Allogeneic (donor-derived, such as umbilical cord blood or other sources).
- Based on the source, stem cells may be:
- Informed Consent:
- Detailed discussions about the therapy, risks, and potential outcomes, followed by signing consent forms.
2. Harvesting Stem Cells (if Autologous)
- Bone Marrow Aspiration:
- Performed under local or general anesthesia.
- A needle is used to extract bone marrow, usually from the pelvic bone.
- Adipose Tissue Extraction:
- A small amount of fat is removed, typically from the abdomen, using a minimally invasive liposuction procedure.
- Peripheral Blood Collection (if applicable):
- Blood is drawn, and stem cells are separated using apheresis.
3. Processing and Preparation
- Isolation and Culturing:
- Stem cells are processed in a laboratory to ensure purity and viability.
- Quality Control:
- The cells are tested for contamination and prepared for administration.
4. Administration of Stem Cells
The method of delivering stem cells varies based on the treatment protocol and medical center:
Intravenous (IV) Infusion:
- The most common and minimally invasive method.
- Stem cells are infused directly into a vein, allowing them to travel through the bloodstream and potentially target areas of inflammation or dysfunction.
Intrathecal (Spinal) Injection:
- Stem cells are injected into the cerebrospinal fluid via a lumbar puncture.
- This method aims to directly deliver stem cells closer to the brain and nervous system.
- Performed under local or general anesthesia to minimize discomfort.
Intranasal Administration (Less Common):
- Stem cells are delivered via the nasal cavity, allowing them to bypass the blood-brain barrier and reach the central nervous system.
5. Post-Treatment Observation
- Immediate Monitoring:
- The patient is observed for a few hours or overnight for any adverse reactions, such as fever, nausea, or allergic responses.
- Discharge Instructions:
- Patients are advised on activity restrictions and follow-up care.
6. Follow-Up and Rehabilitation
- Therapeutic Support:
- Continuation of behavioral therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy to enhance potential benefits.
- Progress Monitoring:
- Regular follow-ups with the medical team to evaluate improvements in symptoms and address any complications.
- Additional Cycles (if needed):
- Some protocols may recommend multiple stem cell therapy sessions spaced over weeks or months.
Expected Duration
- The entire process, from harvesting to administration, may take several days to weeks, depending on the type of stem cells used and the protocol.
Risks and Safety
- Potential Side Effects:
- Fever, fatigue, or local pain at the injection site.
- Rare but serious risks include infection, immune reactions, or neurological complications.
- Experimental Nature:
- Stem cell therapy for autism is not yet conclusively proven, and outcomes can vary.
Key Considerations
- Ensure the therapy is conducted at an accredited and reputable medical center.
- Be realistic about outcomes, as the efficacy of stem cell therapy for autism is still being researched.
- Regular therapies, such as behavioral and speech therapy, remain crucial alongside stem cell treatment.
If you are considering stem cell therapy, consult with specialists to determine if this treatment is appropriate for your child’s specific needs
post procedure
What will be the Post-Care for stem cell therapy for Autism?
Post-Care for Stem Cell Therapy in Autism
Post-care after stem cell therapy for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is a critical part of the treatment process. It ensures the safety of the patient, helps monitor progress, and optimizes potential benefits. Here's what the post-treatment care typically involves:
1. Immediate Post-Treatment Care
- Observation Period:
- After the procedure, the patient is observed for a few hours to ensure there are no immediate adverse reactions, such as fever, nausea, or pain.
- Pain Management:
- If bone marrow or adipose tissue was harvested, mild pain or discomfort at the extraction site might occur. Over-the-counter pain relievers may be recommended.
- Rest:
- The patient may need rest for 1–2 days, depending on the method of administration (e.g., intravenous or intrathecal).
2. Monitor for Side Effects
- Common Side Effects:
- Mild fever, fatigue, headache, or local pain at the injection or harvesting site.
- Serious Reactions:
- Rare but possible issues include infection, allergic reactions, or neurological symptoms (especially with intrathecal injections). Contact your doctor immediately if these occur.
- Follow-Up Appointments:
- Schedule regular follow-ups to monitor for any delayed side effects or complications.
3. Supportive Therapies
- Behavioral Therapy:
- Continue or start Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), cognitive behavioral therapy, or similar interventions to reinforce social, communication, and behavioral skills.
- Speech Therapy:
- Helps improve verbal and non-verbal communication, building on any progress from the stem cell therapy.
- Occupational Therapy:
- Focuses on sensory integration, motor skills, and daily living skills.
- Educational Support:
- Work with educators to tailor learning strategies to the child’s evolving needs.
4. Lifestyle Adjustments
- Diet and Nutrition:
- A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients supports overall health and recovery. Some clinicians may recommend supplements (e.g., omega-3 fatty acids) if beneficial.
- Hydration:
- Encourage adequate fluid intake to support cellular health and recovery.
- Physical Activity:
- Light physical activities may be encouraged, but strenuous activities should be avoided for a few days, especially after intrathecal injections or harvesting procedures.
5. Emotional and Psychological Support
- Counseling:
- Parents and caregivers may benefit from counseling or support groups to manage expectations and emotional challenges.
- Social Skills Groups:
- Enroll the child in programs that help with interaction and communication in structured group settings.
6. Progress Tracking
- Document Changes:
- Maintain a journal to record behavioral, communication, and social changes post-treatment. This helps monitor progress and share observations with healthcare providers.
- Regular Assessments:
- Repeat developmental and behavioral evaluations at intervals (e.g., 3 months, 6 months, and 12 months post-therapy) to assess improvements and plan additional interventions.
7. Long-Term Care
- Additional Cycles:
- Some treatment protocols recommend additional stem cell therapy sessions over months or years. Your doctor will advise based on progress and medical assessments.
- Multidisciplinary Approach:
- Work with a team of specialists, including pediatricians, neurologists, and therapists, for holistic care.
8. Addressing Expectations
- Realistic Outcomes:
- Improvements may take weeks to months to manifest, and results vary widely among individuals. Some children may show noticeable changes in communication, behavior, or sensory responses, while others may have minimal or no changes.
- Patience and Persistence:
- Combine stem cell therapy with consistent therapeutic interventions to maximize the potential for positive outcomes.
When to Seek Medical Help
Contact your healthcare provider immediately if the patient experiences:
- Persistent fever or fatigue.
- Severe headaches, dizziness, or seizures.
- Signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge at the injection or harvesting site.
- Unusual changes in behavior or neurological symptoms.
Key Takeaways
- Post-care is essential to ensure the safety and success of stem cell therapy.
- Regular therapies like behavioral, speech, and occupational therapy remain critical for sustained progress.
- Monitor the patient closely for any side effects and keep communication open with the medical team.
- Manage expectations and focus on long-term, holistic support for the patient.
By maintaining a structured and supportive post-care plan, you can help maximize the potential benefits of stem cell therapy for autism.
success rate
What will be the Success Rate for stem cell therapy for Autism?
Success Rate for Stem Cell Therapy in Autism
The success rate of stem cell therapy for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) is currently not well-established due to its experimental nature and the lack of large-scale, long-term clinical trials. Outcomes vary widely among individuals, and the treatment is not universally effective. Here's an overview of what is known about the potential success and limitations:
Factors Influencing Success
-
Severity of Autism:
- Children with milder symptoms may show more noticeable improvements in social interaction, communication, or behavior.
-
Type of Stem Cells Used:
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) from sources like bone marrow, adipose tissue, or umbilical cord blood are the most commonly studied. These cells are believed to have anti-inflammatory and regenerative properties that may help improve neurological function.
-
Delivery Method:
- Intravenous (IV) or intrathecal (spinal) administration may influence the treatment's efficacy. Intrathecal delivery is thought to target the central nervous system more directly.
-
Age of the Patient:
- Younger children may respond better, as their brains are still developing and might be more receptive to regenerative treatments.
-
Complementary Therapies:
- The combination of stem cell therapy with behavioral, speech, or occupational therapies often yields better outcomes.
-
Underlying Medical Issues:
- Children with co-existing conditions, such as epilepsy or severe immune dysfunction, may have variable responses to treatment.
Reported Improvements
While scientific evidence is limited, anecdotal reports and small studies have documented some improvements in the following areas:
- Social Interaction: Increased eye contact, better social engagement, and improved response to social cues.
- Communication Skills: Enhanced verbal abilities, increased vocabulary, and improved clarity of speech.
- Behavioral Symptoms: Reduced hyperactivity, aggression, and irritability.
- Cognitive Abilities: Improved focus, problem-solving, and learning capacity.
- Sensory Sensitivities: Better tolerance to sensory stimuli, such as sounds, lights, and textures.
Limitations and Concerns
-
Lack of Standardization:
- Different clinics use varying protocols, making it difficult to compare outcomes or establish a definitive success rate.
-
Small-Scale Studies:
- Most studies have been conducted on small groups, with limited follow-up periods. Results are often anecdotal and not peer-reviewed.
-
Unpredictable Results:
- Some individuals show noticeable improvements, while others experience minimal or no changes.
-
Placebo Effect:
- In some cases, perceived improvements may be due to the placebo effect or increased attention to therapies post-treatment.
-
Risks and Ethical Concerns:
- The experimental nature of the therapy raises concerns about safety, especially in clinics without proper regulatory oversight.
Current Research Findings
- A few studies have reported improvements in behavioral symptoms and quality of life, but these results are preliminary and not conclusive.
- Clinical trials are ongoing worldwide to better understand the potential of stem cell therapy for autism, including its mechanisms, safety, and efficacy.
Estimated Success Rates
While exact success rates are not available, anecdotal reports and small studies suggest:
- Mild to Moderate Autism: Approximately 40–60% of children may show some improvement in symptoms, but the degree of improvement varies.
- Severe Autism: Lower success rates are reported, with improvements generally focused on reducing irritability or aggression rather than enhancing communication or social skills.
Realistic Expectations
- Not a Cure: Stem cell therapy is not a cure for autism. At best, it may alleviate certain symptoms or improve quality of life.
- Complementary Treatment: It should be viewed as part of a broader, multidisciplinary approach, including traditional therapies.
- Gradual Changes: Improvements, if they occur, may take weeks to months to become noticeable.
Conclusion
Stem cell therapy for autism is still in the experimental stage, and its success cannot be guaranteed. Families considering this treatment should:
- Consult with reputable medical professionals.
- Choose accredited centers that follow ethical and scientific guidelines.
- Combine the therapy with evidence-based treatments for the best outcomes.
- Monitor the child’s progress and maintain realistic expectations about the results.
Continuing advancements in research may provide clearer insights into the success rates and mechanisms of stem cell therapy for autism in the future.
faqs from doctor
FAQs for Stem Cell Therapy for Autism in India
Here’s a comprehensive list of frequently asked questions (FAQs) about stem cell therapy for Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) in India:
General Questions
1. What is stem cell therapy for autism?
Stem cell therapy is an experimental treatment that involves using stem cells to repair, regenerate, or modulate dysfunctional neural pathways associated with autism. The therapy aims to reduce inflammation in the brain and promote neural development.
2. Is stem cell therapy for autism approved in India?
Stem cell therapy for autism is classified as experimental in India. It is not yet approved as a standard treatment but is allowed under specific clinical research guidelines overseen by the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) and the Central Drugs Standard Control Organization (CDSCO).
3. Who is eligible for stem cell therapy for autism?
Eligibility is determined after a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, developmental progress, and behavioral symptoms. Typically, individuals with ASD showing significant deficits in social, communication, or behavioral skills may be considered.
Procedure-Related Questions
4. How are stem cells administered?
Stem cells are administered via:
- Intravenous (IV) infusion: Through a vein.
- Intrathecal injection: Into the cerebrospinal fluid via the spine.
- Intranasal delivery: (Less common) through the nasal cavity.
5. What types of stem cells are used for autism therapy?
- Autologous stem cells: Derived from the patient’s own body (e.g., bone marrow or adipose tissue).
- Allogeneic stem cells: Donor-derived cells, such as umbilical cord blood stem cells.
6. How long does the procedure take?
The duration depends on the method of administration:
- Stem Cell Harvesting: 1–2 hours (if autologous).
- Processing and Administration: 1–3 days.
7. Is stem cell therapy painful?
Most procedures, such as IV infusion, are minimally invasive and painless. If harvesting is required (e.g., bone marrow aspiration), mild discomfort may occur but is usually managed with local or general anesthesia.
Cost and Availability
8. How much does stem cell therapy for autism cost in India?
The cost ranges from 8000 to 15000 USD or more, depending on:
- The type and source of stem cells used.
- The treatment center and its location.
- The number of therapy cycles recommended.
9. Are there specialized centers for stem cell therapy for autism in India?
Yes, some reputed centers include:
- NeuroGen Brain and Spine Institute, Mumbai.
- Advancells, Noida.
- StemRx Bioscience Solutions, Navi Mumbai.
- Nutech Mediworld, Delhi.
10. Is stem cell therapy covered by insurance in India?
No, stem cell therapy for autism is not covered by insurance in India because it is still considered experimental.
Effectiveness and Safety
11. Is stem cell therapy a cure for autism?
No, stem cell therapy is not a cure for autism. It is aimed at improving specific symptoms, such as communication, social interaction, and behavior.
12. What are the success rates for stem cell therapy in autism?
The success rate is variable. Some studies report improvements in 40–60% of cases for mild to moderate autism, but outcomes differ widely. Long-term efficacy is still under research.
13. Are there risks or side effects?
Common side effects include:
- Mild fever.
- Local pain at the injection site.
- Rare risks include infection, immune reactions, or neurological complications.
Post-Treatment Care
14. What is the recovery time after therapy?
Most patients resume normal activities within a day or two after the procedure. Full recovery from any harvesting process (if applicable) may take up to a week.
15. How long does it take to see results?
Results may take several weeks to months, and the degree of improvement varies. Some children show changes in behavior, communication, or sensory responses over 6–12 months.
Regulations and Ethics
16. Is stem cell therapy for autism ethical?
The treatment is considered ethical if conducted under approved clinical trials or research protocols. Families should ensure they are working with accredited and licensed medical centers.
17. How can I verify the credibility of a treatment center in India?
- Check if the center is accredited by the National Accreditation Board for Hospitals & Healthcare Providers (NABH).
- Confirm adherence to ICMR and CDSCO guidelines.
- Review patient testimonials and published clinical trial data (if available).
Decision-Making
18. Should I try stem cell therapy for my child with autism?
This decision depends on:
- The severity of your child’s symptoms.
- Consultation with medical professionals.
- Understanding the experimental nature, costs, and potential risks of the therapy.
19. What should I do if I’m interested in stem cell therapy for autism?
- Consult a developmental pediatrician or neurologist.
- Contact reputable stem cell therapy centers for detailed evaluations.
- Research the treatment protocols, costs, and expected outcomes.
20. Are there alternatives to stem cell therapy?
Yes, evidence-based alternatives include:
- Behavioral Therapies: Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), speech therapy, and occupational therapy.
- Medications: For managing specific symptoms like hyperactivity or anxiety.
- Nutritional Support: Diet modifications and supplements.
Final Note
Stem cell therapy for autism in India is a promising but experimental approach. Families should consult trusted medical experts and carefully evaluate the potential benefits and risks before proceeding.
Top Doctors
Sorry, There is nothing to show!Come back soon.















