Duration of Treatment
usually takes 4 to 6 hours depending on size.
Days of Stay
usually 5 to 10 days at the hospital and 2 months outside the hospital.
Anesthesia
General anesthesia.
Cost
5000 to 7000 USD
How Much Does Brain Tumour Surgery Cost in India?
are you looking for a Brain Tumour Surgery Cost in India or a Top 10 Neurosurgeon at an affordable cost in different cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, and Bangalore? Here, we answer the question and explain how to choose the top 10 brain tumor treatment centers in India for better results. Still, have questions? SUBMIT ENQUIRY
We have also shortlisted the list of top 10 brain tumor treatment centers in India and Surgeons on the basis of Hospital accreditations, experience & qualification of surgeons, success rates of procedures, and patient testimonials.
- Brain Tumour Surgery Cost in India: Starting from 5,000 to 7,000 USD
- Radiation Therapy Cost: Starting from 3,800 to 5800 USD
- Chemotherapy Cost: Starting from 300 to 600 USD (per cycle depending on drug choice)
- Cyberknife Surgery Cost: Starting from 7,000 to 9,000 USD
- GamaKnife Surgery Cost: Starting from 5,000 to 7,000 USD ( 1-2 fractionation)
- Hotel Cost Near Hospital - starting from 18 to 50 USD ( as per hotel services)
- Food Cost - starting from 20 to 30 USD (per day )
- Miscellaneous cost - 20 USD (per day)
- It's only a rough estimate, final treatment will plan after the fresh evaluation reports.
- Brain Tumor Surgery cost in India can vary as per the diagnosis, patient's conditions, surgeon experience, Implant quality, hospital facilities, and city.
- To make an appointment, learn more about brian, read the below information, or call / WhatsApp/ Viber - our experts to answer at +91 9582708782. Still, have questions?
Who is the Top 10 NeuroSurgeon in India?
- Dr. Bipin Walia
- Dr. Rana Patir
- Dr. Anil Kumar Kansa
- Dr. Vikas Gupta
- Dr. Aditya Gupta
- Dr. Sunit Mediratta
- Dr. Rahul Gupta
- Dr. Arun Saroha
- Dr. Anandh Balasubramaniam
- Dr. Shibu Vasudevan Pillai
Which is the best neurosurgery hospital in India?
- ARTEMIS HOSPITAL
- MANIPAL HOSPITAL
- BLK HOSPITAL
- APOLLO HOSPITAL
- FORTIS HOSPITAL
- MAX HOSPITAL
- MEDANTA HOSPITAL
- YASHODHA HOSPITAL
- GLOBAL HOSPITAL
- NARAYANA HOSPITAL
Why did you choose Peace Medical Tourism?
We are one of the best health care services providers with more than 10 years of experience to provide the best treatment at an affordable cost and guide our international patients to choose the top destination as per patient's budget and treatment.
- Comprehensive and 100% transparency.
- Help to Choose the Best top 10 brain tumor treatment centers.
- Very highly skilled Neurosurgeon in India team.
- World-class technology for surgery.
- The high success rate of procedures with international standards.
- Affordable Cost of brain surgery in India.
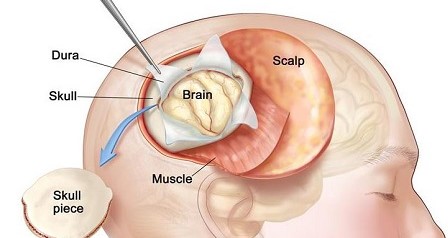
What is Brain Tumour Surgery?
Brain Tumor Surgery is a medical procedure used to remove or reduce a tumor in the brain. It is one of the primary treatments for brain tumors, aimed at either completely removing the tumor or alleviating symptoms caused by its presence, such as pressure on the brain or interference with its functions.
The brain serves as the control center for the entire body, and a brain tumor refers to a mass of abnormal cells that grow within or near the brain.
Types of Brain Tumors
-
Benign Tumors (Non-Cancerous):
- Characteristics:
- Grow slowly.
- Remain localized (do not spread to other parts of the body).
- Can usually be safely removed via surgery.
- Examples: Meningiomas, Schwannomas, and Pituitary Adenomas.
- Characteristics:
-
Malignant Tumors (Cancerous):
- Characteristics:
- Grow rapidly.
- Can invade nearby brain tissue or spread to other parts of the central nervous system (brain or spinal cord).
- Known as brain metastases when cancer spreads to the brain from other organs.
- Examples: Glioblastoma Multiforme, Astrocytomas, and Metastatic Brain Tumors.
- Characteristics:
Purpose of Brain Tumor Surgery
- Diagnostic Biopsy: To determine the type and grade of the tumor.
- Tumor Removal: To excise as much of the tumor as safely possible while preserving neurological function.
- Symptom Relief: To reduce pressure on the brain caused by the tumor.
- Improving Quality of Life: To manage symptoms like headaches, seizures, or neurological deficits.
Types of Brain Tumor Surgeries
-
Craniotomy:
- Involves removing a portion of the skull to access the tumor and then replacing the bone after surgery.
-
Endoscopic Surgery:
- Minimally invasive technique using an endoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera) to access the tumor.
-
Stereotactic Surgery:
- Uses imaging techniques (MRI or CT scans) to precisely locate the tumor for minimally invasive procedures or biopsies.
-
Laser Ablation:
- A minimally invasive procedure using lasers to destroy tumor cells.
-
Awake Brain Surgery:
- Performed while the patient is awake to monitor and preserve critical brain functions during tumor removal.
-
Shunt Placement:
- To relieve fluid build-up (hydrocephalus) often caused by tumors.
Factors Affecting Surgery
- Location: Tumors in critical areas of the brain may require specialized techniques.
- Size and Type: Larger or malignant tumors may involve more complex surgery or additional treatments like radiation or chemotherapy.
- Patient’s Health: General health and neurological condition influence the surgical approach and recover
What do Brain Tumor surgery signs include?
Signs and Symptoms Indicating the Need for Brain Tumor Surgery
Brain tumor surgery is often recommended when a tumor in the brain causes symptoms or poses risks to the patient's health. Symptoms vary depending on the size, location, and type of tumor. Below are the key signs that may indicate the presence of a brain tumor and necessitate surgical intervention:
Common Symptoms of Brain Tumors
-
Headaches:
- Persistent or severe headaches, especially those that worsen in the morning or with activity.
- Headaches that do not respond to standard pain medications.
-
Seizures:
- Sudden, unexplained seizures, even in individuals with no prior history of epilepsy.
- Seizures may vary in type, from muscle jerking to loss of consciousness.
-
Neurological Deficits:
- Weakness or Paralysis: Difficulty moving a limb or one side of the body.
- Vision Changes: Blurred or double vision, loss of peripheral vision, or sudden blindness.
- Speech Problems: Difficulty speaking, understanding language, or slurred speech.
- Hearing Issues: Hearing loss or ringing in the ears (tinnitus).
-
Cognitive or Behavioral Changes:
- Memory problems, confusion, or difficulty concentrating.
- Changes in personality, mood swings, or unusual behavior.
-
Balance and Coordination Issues:
- Difficulty walking, maintaining balance, or performing fine motor tasks like writing.
-
Nausea and Vomiting:
- Persistent nausea or vomiting not related to other conditions, often worse in the morning.
-
Swelling or Pressure Symptoms:
- Signs of increased intracranial pressure, such as drowsiness, confusion, or unresponsiveness.
-
Fatigue:
- Constant tiredness or lack of energy unrelated to sleep or exertion.
When Surgery is Needed
Brain tumor surgery may be required if:
- The tumor is causing significant pressure on the brain.
- The tumor is located in an accessible area where it can be safely removed.
- Symptoms are severe and progressive, affecting the patient's quality of life.
- A biopsy is needed to confirm the tumor's type and grade.
- The tumor is cancerous and needs to be removed as part of comprehensive treatment.
Urgent Signs Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
- Sudden loss of consciousness.
- Rapid neurological decline (e.g., inability to speak, paralysis).
- Severe, unrelenting headaches accompanied by vomiting or confusion.
Conclusion
The symptoms associated with brain tumors often mimic those of other conditions, so an accurate diagnosis through imaging (CT scan, MRI) and evaluation by a neurologist or neurosurgeon is critical. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve outcomes and reduce complications.
What does Brain Tumor surgery risk factor include?
Brain Tumor Surgery Risk Factors
Brain tumor surgery, while potentially life-saving, carries certain risks due to the complexity and sensitivity of operating on the brain. These risks depend on factors such as the tumor's size, location, type, and the patient’s overall health. Below are the key risk factors associated with brain tumor surgery:
General Risks of Surgery
-
Bleeding (Hemorrhage):
- Excessive bleeding can occur during or after surgery, particularly in areas with abundant blood vessels.
-
Infection:
- Infection of the incision site or within the brain (e.g., meningitis) is a potential risk.
-
Blood Clots:
- Patients may develop blood clots, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), during the recovery period.
Neurological Risks
-
Brain Swelling (Edema):
- Swelling around the surgical site can increase intracranial pressure and cause complications.
-
Seizures:
- Surgery may irritate brain tissue, leading to seizures post-operatively.
-
Neurological Deficits:
- Depending on the tumor's location, surgery may result in:
- Weakness or Paralysis: Especially if the tumor is near the motor cortex.
- Speech Difficulties: If the tumor is near language centers.
- Vision or Hearing Loss: If areas of the brain related to sight or hearing are affected.
- Balance or Coordination Issues: If the cerebellum is involved.
- Depending on the tumor's location, surgery may result in:
-
Cognitive Impairments:
- Memory problems, difficulty concentrating, or changes in behavior/personality can result from damage to specific brain areas.
Surgical Complications
-
Incomplete Tumor Removal:
- In some cases, the entire tumor cannot be removed due to its location near critical brain structures, leaving residual tumor tissue that may require further treatment.
-
CSF Leaks:
- Leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) can occur, increasing the risk of infection.
-
Hydrocephalus:
- Accumulation of fluid in the brain may necessitate a shunt to relieve pressure.
-
Stroke:
- Damage to blood vessels during surgery can result in a stroke.
-
Coma or Death:
- Rare but severe outcomes can occur if complications arise during or after surgery.
Factors That Increase Risks
-
Tumor Location:
- Tumors near vital structures like the brainstem, optic nerve, or motor areas pose higher surgical risks.
-
Tumor Size:
- Larger tumors may require more extensive surgery, increasing the potential for complications.
-
Patient Age:
- Older patients are more vulnerable to surgical complications and slower recovery.
-
Underlying Health Conditions:
- Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or previous strokes can complicate surgery and recovery.
-
Malignant Tumors:
- Aggressive, fast-growing tumors may require more invasive procedures, increasing risk.
Post-Surgical Risks
-
Recurrence:
- Incomplete removal or the aggressive nature of some tumors can lead to recurrence.
-
Dependency on Rehabilitation:
- Some patients may require long-term physical, occupational, or speech therapy to regain lost functions.
-
Psychological Impact:
- Surgery and its potential effects can cause anxiety, depression, or other emotional challenges.
Minimizing Risks
- Choosing an experienced neurosurgeon and hospital with advanced technology (e.g., intraoperative MRI, neuronavigation).
- Pre-surgical evaluations and imaging to plan the safest approach.
- Post-operative monitoring in an ICU setting for early detection of complications.
- Rehabilitation and regular follow-ups to address any deficits or residual issues.
Conclusion
Brain tumor surgery in India involves inherent risks, but advancements in neurosurgical techniques and technologies have significantly improved safety and outcomes. Understanding these risks and working closely with a skilled medical team helps ensure the best possible results.
How do you prepare for brain tumor surgery?
Preparing for brain tumor surgery involves both medical and practical steps to ensure the procedure is as safe and effective as possible. Below is a detailed guide on how to prepare:
1. Choose the Best Option for Surgery
- Research and select a highly experienced neurosurgeon and a reputable hospital in your city or abroad.
- Consider factors like hospital accreditation, surgeon experience, success rates, and patient testimonials.
- Discuss your specific condition and surgical options with your doctor.
2. Pre-Surgery Check-Up (PSC)
- Diagnostic Tests:
- Blood Tests: To check for infections, clotting ability, and overall health.
- ECG (Electrocardiogram) and ECHO: To ensure the heart is healthy enough for surgery.
- Urine Tests: To rule out infections or abnormalities.
- Imaging Studies: MRI or CT scans to map the tumor and plan the surgical approach.
- Assessment:
- The results will determine if you are fit for surgery.
3. Pre-Surgical Instructions
-
Consent Form:
- You’ll be required to sign a consent form giving the surgeon permission to perform the surgery.
-
Medication Review:
- Inform your doctor about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies.
- Stop blood thinners (e.g., aspirin, warfarin, clopidogrel) at least 7–10 days before surgery to reduce the risk of excessive bleeding.
-
Fasting:
- You will be advised to avoid food and drinks (fasting) for 8–12 hours before the procedure.
4. Lifestyle Adjustments Before Surgery
- Quit Smoking and Alcohol:
- These can affect healing and anesthesia safety.
- Healthy Diet:
- Eat a nutritious diet leading up to surgery to boost immunity and recovery.
5. Admission to the Hospital
- You will typically be admitted on the day of the procedure or the day before.
- The medical team will review your test results and provide final instructions.
6. Mental and Emotional Preparation
- Discuss any concerns or questions with your doctor.
- Engage in relaxation techniques like meditation to ease anxiety.
- Speak with a counselor, if needed, to address emotional concerns.
Cost of Brain Tumor Surgery in India
- Estimated Cost: $5,000 to $7,000 USD.
- This can vary based on factors such as:
- Surgeon’s Experience
- Hospital Facilities
- City (Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, Chennai, etc.)
- Patient’s Condition and complexity of the procedure.
- This can vary based on factors such as:
Why Choose India for Brain Tumor Surgery?
- Affordable Cost compared to Western countries.
- Availability of world-class hospitals with advanced facilities.
- Highly skilled and experienced neurosurgeons.
- Excellent patient care and recovery support.
Top Tips
- Follow all pre-surgical instructions provided by your healthcare team.
- Arrange for a trusted family member or friend to accompany you and assist during recovery.
- Discuss post-surgery recovery plans, including rehabilitation, with your doctor in advance.
Proper preparation for brain tumor surgery in India is essential for the best surgical outcomes and a smoother recovery process.
How is the Brain Tumour Surgery Procedure done?
Brain Tumor Surgery and Treatment Procedures
Brain tumor treatment depends on the type, size, and location of the tumor as well as the patient’s overall health. Below is a detailed explanation of the procedures and techniques used for brain tumor surgery and related treatments:
1. Brain Tumor Surgery
The primary method for treating brain tumors is surgical removal.
Procedure:
-
Incision:
- A neurosurgeon makes an incision in the scalp and removes a section of the skull (craniotomy) to access the brain.
-
Tumor Removal:
- Using advanced imaging techniques (e.g., intraoperative MRI or CT scans), the surgeon locates the tumor.
- Depending on its location, part or all of the tumor is removed:
- Complete Resection: When the tumor is in an accessible area and can be fully removed.
- Partial Resection: If the tumor is near vital brain structures, only a portion may be safely removed.
-
Closing:
- After the tumor removal, the skull section is replaced, and the incision is closed with sutures or staples.
Goals:
- Relieve symptoms caused by the tumor (e.g., headaches, seizures).
- Reduce pressure in the brain.
- Remove as much of the tumor as possible without causing damage to healthy brain tissue.
2. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells and shrink tumors.
Procedure:
- External Beam Radiation:
- Delivered over multiple sessions using focused radiation beams.
- Used to treat residual tumor cells after surgery.
- Benefits:
- Controls tumor growth and prevents recurrence.
- Especially useful for inoperable tumors or cancer that has spread (metastasized).
3. Radiosurgery
Radiosurgery is a non-invasive treatment that uses targeted radiation to treat small tumors or lesions.
Types:
- Gamma Knife Surgery:
- Delivers highly focused gamma rays to a specific area of the brain.
- Ideal for small tumors or lesions near critical structures.
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery:
- Uses advanced imaging and computer technology to precisely deliver radiation.
- Minimizes damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Procedure:
- Performed as an outpatient (daycare) procedure.
- Does not involve surgical incisions.
- Patients can return to normal activities quickly.
4. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves using drugs to destroy or control the growth of cancer cells.
Procedure:
- Administered orally, intravenously, or through wafers placed directly in the brain during surgery.
- Often combined with surgery and radiation therapy to improve outcomes.
Goals:
- Shrink tumors before surgery.
- Eliminate residual cancer cells post-surgery.
- Prevent tumor recurrence.
5. Targeted Drug Therapy
This treatment focuses on specific molecular changes in cancer cells to stop their growth.
Common Drugs:
- Bevacizumab (Avastin):
- Inhibits blood vessel formation in tumors, cutting off their nutrient supply.
- Everolimus (Afinitor):
- Targets specific proteins involved in tumor growth.
Role:
- Often used for recurrent tumors or when standard therapies are ineffective.
- Typically a supplementary treatment rather than a primary one.
Considerations for Choosing a Treatment Plan
- Tumor Type:
- Benign or malignant.
- Primary or metastatic.
- Tumor Location:
- Accessibility and proximity to vital brain structures.
- Patient Condition:
- Age, overall health, and tolerance to treatments.
- Goals of Treatment:
- Symptom relief, life extension, or improving quality of life.
Conclusion
Brain tumor treatment often involves a combination of surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Emerging technologies like radiosurgery and targeted therapies further improve outcomes, especially for complex or advanced cases. Choosing the right treatment plan requires collaboration with a skilled neurosurgeon and a multidisciplinary medical team.
What is the Brain Tumour Post Surgery Care?
Post-Surgery Care for Brain Tumor Patients
Proper care following brain tumor surgery is essential for recovery and minimizing complications. Below is a detailed guide on post-operative care:
1. Hospital Stay and Immediate Recovery
-
Monitoring:
- After surgery, patients are kept in the intensive care unit (ICU) for close monitoring of vital signs and neurological function.
- The medical team observes for any signs of complications, such as swelling, bleeding, or infection.
-
Pain Management:
- Medications will be prescribed to manage pain and discomfort.
- Anti-seizure medications may also be given to prevent seizures.
-
Initial Mobilization:
- Patients are encouraged to move around gently as soon as it is safe to prevent blood clots and promote circulation.
2. Care of Incisions
- Cleaning and Dressing:
- The surgical site must be kept clean and dry.
- Dressings should be changed as per the surgeon's instructions.
- Stitches or Staples:
- Stitches or staples are typically removed 7 to 10 days after surgery during a follow-up visit.
- Signs of Infection:
- Monitor the incision for redness, swelling, or discharge.
- Report any fever or unusual symptoms to the doctor immediately.
3. Medications
- Pain Relievers: To control postoperative pain.
- Antibiotics: To prevent infection.
- Anti-Seizure Medications: Often prescribed, especially if the patient had seizures before surgery or the tumor affected brain areas linked to seizures.
- Steroids: To reduce brain swelling and inflammation.
4. Physical and Neurological Recovery
-
Physical Therapy:
- Helps patients regain strength, balance, and mobility.
-
Occupational Therapy:
- Aids in adapting to daily tasks and routines if motor or cognitive functions are affected.
-
Speech Therapy:
- Recommended for patients with difficulty speaking or swallowing due to surgery.
-
Cognitive Rehabilitation:
- Focuses on improving memory, attention, and problem-solving skills.
5. Activity Restrictions
-
Avoid Heavy Lifting:
- Refrain from strenuous activities, heavy lifting, or intense physical exertion for several weeks.
-
Driving:
- Driving is not recommended until cleared by the surgeon, especially for those on anti-seizure medications.
-
Rest and Sleep:
- Ensure adequate rest to aid healing, but gradually increase activity levels as advised by the doctor.
6. Follow-Up Appointments
- Regular follow-ups with the neurosurgeon to monitor healing and discuss any concerns.
- Additional MRI or CT scans may be done to ensure no tumor remnants remain and to assess recovery.
7. Lifestyle Adjustments
- Diet:
- Follow a balanced, nutritious diet to promote healing and strengthen the immune system.
- Hydration:
- Drink plenty of fluids unless otherwise restricted by the doctor.
- Smoking and Alcohol:
- Avoid smoking and alcohol as they can interfere with healing.
8. Emotional and Psychological Support
- Emotional Well-Being:
- Surgery and recovery can be emotionally taxing. Counseling or therapy can help manage stress and anxiety.
- Support Groups:
- Joining a support group for brain tumor survivors can provide emotional encouragement and shared experiences.
9. Potential Signs to Watch for Post-Surgery
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Severe headaches or sudden changes in mental status.
- Persistent nausea or vomiting.
- Weakness or loss of sensation in any part of the body.
- Difficulty speaking, seeing, or swallowing.
- Seizures.
- Signs of infection (fever, redness, swelling, or discharge from the incision).
10. Long-Term Care
- Depending on the tumor type, additional treatments like radiation or chemotherapy may be necessary.
- Lifelong monitoring may be required to check for tumor recurrence or long-term effects of the surgery.
Proper adherence to post-surgery care instructions significantly impacts recovery outcomes and quality of life. Always maintain open communication with your medical team for the best guidance.
What is the Brain Tumour Surgery Success Rate?
Brain Tumor Surgery Success Rate
The success of brain tumor surgery depends on several factors, including the type, size, location, and stage of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health and age. Here’s a breakdown of the key factors and outcomes:
1. Success Rate Overview
-
Benign Tumors (Non-Cancerous):
- Surgery for benign tumors has a high success rate, often exceeding 90% when the tumor is accessible and completely removed.
- Patients generally experience full recovery, especially if the tumor has not caused significant neurological damage.
-
Malignant Tumors (Cancerous):
- The success rate varies depending on the type and grade of the tumor.
- For low-grade gliomas, the survival rate is relatively high, with many patients living beyond 5 years.
- High-grade gliomas, such as glioblastomas, are more challenging to treat. Surgery can help alleviate symptoms and prolong survival but is rarely curative.
2. Factors Influencing Success
-
Tumor Accessibility:
- Tumors in areas of the brain that are easily reachable and not near critical structures have higher removal success rates.
- Deep-seated or complex tumors near vital regions may require partial removal to avoid complications.
-
Complete vs. Partial Resection:
- Complete removal often leads to better outcomes and lower recurrence rates.
- Partial removal may require additional treatments, such as radiation or chemotherapy.
-
Patient Health:
- Younger patients and those with no significant comorbidities tend to recover more successfully.
-
Advanced Techniques:
- Use of technologies like intraoperative MRI, neuronavigation, and awake brain surgery significantly increases precision and reduces risks.
3. Additional Treatment Contributions
-
Radiation Therapy:
- Enhances outcomes by targeting residual tumor cells and reducing recurrence risks.
-
Chemotherapy:
- Can prolong survival for certain types of malignant tumors when combined with surgery and radiation.
-
Emerging Therapies:
- Targeted drug therapies and immunotherapies continue to improve the prognosis for patients with specific genetic mutations.
4. Long-Term Outcomes
-
Recurrence:
- Benign tumors, if fully removed, rarely recur.
- Malignant tumors often require lifelong monitoring and ongoing treatments to manage recurrence risks.
-
Quality of Life:
- Many patients experience significant improvement in symptoms such as headaches, seizures, and neurological deficits post-surgery.
5. Estimated Survival Rates
-
Benign Tumors:
- 10-year survival rates are very high, often exceeding 95% with early intervention.
-
Low-Grade Malignant Tumors:
- 5-year survival rates range from 70% to 90%, depending on tumor type and treatment.
-
High-Grade Malignant Tumors:
- Glioblastoma: Median survival is 12–18 months, with a small percentage living beyond 5 years when treated with surgery and adjuvant therapies.
Conclusion
Brain tumor surgery has a high success rate, particularly for benign and early-stage tumors. While malignant tumors present greater challenges, advancements in surgical techniques and supplementary treatments continue to improve outcomes and survival rates. Early diagnosis and treatment remain critical for the best results.
What questions should I ask about a brain tumor?
Answers to Your Brain Tumor Questions
-
Are you a board-certified top neurosurgeon in India?
Yes, always confirm that your neurosurgeon is board-certified and has extensive experience in brain tumor surgeries. You can also inquire about their specialization in specific types of tumors or advanced surgical techniques, and are you Top 10 Neurosurgeon in India -
How many years of experience do you have in this field?
Most top neurosurgeons in India have 15–30 years of experience. Ensure your surgeon has significant expertise in handling complex brain tumor cases. -
Do you have the top 10 brain tumor treatment centers in India?
The leading brain tumor treatment centers in India include AIIMS (Delhi), Apollo Hospitals, Fortis Hospitals, Medanta, and others. A reputable surgeon will typically have affiliations with one or more of these centers. -
How many surgeries are you doing every day for brain tumor surgery?
A highly experienced neurosurgeon may perform 2–3 brain tumor surgeries weekly, depending on the complexity of the cases and the available infrastructure. -
How much does brain tumor surgery cost in India?
The cost ranges from ₹2,00,000 to ₹7,00,000 ($2,500–$9,000), depending on the hospital, surgeon’s expertise, and the complexity of the surgery. -
In India, what is the cost of radiation therapy for brain tumors?
Radiation therapy costs between ₹1,50,000 and ₹3,00,000 ($2,000–$4,000), depending on the type of radiation (e.g., IMRT, CyberKnife, or Proton Therapy). -
Am I a good patient for you for brain tumor surgery?
This depends on factors like tumor type, location, size, your overall health, and prior treatments. Your surgeon will assess these through imaging and medical evaluations. -
What type of brain tumor do I have?
The tumor type is determined through imaging (MRI/CT scans) and biopsy. Common types include gliomas, meningiomas, pituitary tumors, and metastatic brain tumors. -
Let me know the success rates and how long time will take for recovery.
Success rates vary but are generally high for benign tumors (90–95%). Recovery time ranges from 4–8 weeks, depending on the complexity of the surgery and individual health. -
What treatment plan do you recommend and why?
The treatment may involve surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or a combination. The plan depends on the tumor type, grade, location, and overall health. -
What are the advantages and disadvantages of brain tumor surgery?
Advantages: Removal or reduction of the tumor, symptom relief, and potential cure for benign tumors.
Disadvantages: Risks include infection, bleeding, neurological deficits, or recurrence of the tumor. -
How long do I have to stay in and outside the hospital?
Hospital stay is typically 5–7 days, with additional recovery at home for 4–6 weeks. Rehabilitation may be needed in some cases. -
What are the risk factors for this type of surgery?
Risks include infection, blood clots, swelling, seizures, and changes in neurological function like speech or movement. -
When can I go for normal activities, including exercise?
Light activities can resume in 4–6 weeks, but heavy exercise, depending on recovery progress, may require 3–6 months. -
Do I have stitches, staples, and bandages?
Yes, most surgeries involve stitches or staples to close the incision. These are typically removed 10–14 days after surgery. -
Do I need to go for another surgery in the future?
This depends on the tumor type. For benign tumors, additional surgery is rare unless there is a recurrence. Malignant tumors may require further interventions. -
May I know the top 10 brain tumor treatment centers in India?
- ARTEMIS HOSPITAL
- MANIPAL HOSPITAL
- BLK HOSPITAL
- APOLLO HOSPITAL
- FORTIS HOSPITAL
- MAX HOSPITAL
- MEDANTA HOSPITAL
- YASHODHA HOSPITAL
- GLOBAL HOSPITAL
- NARAYANA HOSPITAL
-
Do I need any follow-up appointments or tests after my surgery?
Yes, regular follow-ups and imaging (MRI or CT) are essential to monitor recovery and check for recurrence. These are typically scheduled every 3–6 months initially, then annually.
Top Doctors
Top Hospitals
BRAIN TUMOUR SURGERY COST IN INDIA

Duration of Treatment
usually takes 4 to 6 hours depending on size.
Days of Stay
usually 5 to 10 days at the hospital and 2 months outside the hospital.
Anesthesia
General anesthesia.
Cost
5000 to 7000 USD
How Much Does Brain Tumour Surgery Cost in India?
are you looking for a Brain Tumour Surgery Cost in India or a Top 10 Neurosurgeon at an affordable cost in different cities like Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai, Kolkata, and Bangalore? Here, we answer the question and explain how to choose the top 10 brain tumor treatment centers in India for better results. Still, have questions? SUBMIT ENQUIRY
We have also shortlisted the list of top 10 brain tumor treatment centers in India and Surgeons on the basis of Hospital accreditations, experience & qualification of surgeons, success rates of procedures, and patient testimonials.
- Brain Tumour Surgery Cost in India: Starting from 5,000 to 7,000 USD
- Radiation Therapy Cost: Starting from 3,800 to 5800 USD
- Chemotherapy Cost: Starting from 300 to 600 USD (per cycle depending on drug choice)
- Cyberknife Surgery Cost: Starting from 7,000 to 9,000 USD
- GamaKnife Surgery Cost: Starting from 5,000 to 7,000 USD ( 1-2 fractionation)
- Hotel Cost Near Hospital - starting from 18 to 50 USD ( as per hotel services)
- Food Cost - starting from 20 to 30 USD (per day )
- Miscellaneous cost - 20 USD (per day)
- It's only a rough estimate, final treatment will plan after the fresh evaluation reports.
- Brain Tumor Surgery cost in India can vary as per the diagnosis, patient's conditions, surgeon experience, Implant quality, hospital facilities, and city.
- To make an appointment, learn more about brian, read the below information, or call / WhatsApp/ Viber - our experts to answer at +91 9582708782. Still, have questions?
Who is the Top 10 NeuroSurgeon in India?
- Dr. Bipin Walia
- Dr. Rana Patir
- Dr. Anil Kumar Kansa
- Dr. Vikas Gupta
- Dr. Aditya Gupta
- Dr. Sunit Mediratta
- Dr. Rahul Gupta
- Dr. Arun Saroha
- Dr. Anandh Balasubramaniam
- Dr. Shibu Vasudevan Pillai
Which is the best neurosurgery hospital in India?
- ARTEMIS HOSPITAL
- MANIPAL HOSPITAL
- BLK HOSPITAL
- APOLLO HOSPITAL
- FORTIS HOSPITAL
- MAX HOSPITAL
- MEDANTA HOSPITAL
- YASHODHA HOSPITAL
- GLOBAL HOSPITAL
- NARAYANA HOSPITAL
Why did you choose Peace Medical Tourism?
We are one of the best health care services providers with more than 10 years of experience to provide the best treatment at an affordable cost and guide our international patients to choose the top destination as per patient's budget and treatment.
- Comprehensive and 100% transparency.
- Help to Choose the Best top 10 brain tumor treatment centers.
- Very highly skilled Neurosurgeon in India team.
- World-class technology for surgery.
- The high success rate of procedures with international standards.
- Affordable Cost of brain surgery in India.
What is Brain Tumour Surgery?
Brain Tumor Surgery is a medical procedure used to remove or reduce a tumor in the brain. It is one of the primary treatments for brain tumors, aimed at either completely removing the tumor or alleviating symptoms caused by its presence, such as pressure on the brain or interference with its functions.
The brain serves as the control center for the entire body, and a brain tumor refers to a mass of abnormal cells that grow within or near the brain.
Types of Brain Tumors
-
Benign Tumors (Non-Cancerous):
- Characteristics:
- Grow slowly.
- Remain localized (do not spread to other parts of the body).
- Can usually be safely removed via surgery.
- Examples: Meningiomas, Schwannomas, and Pituitary Adenomas.
- Characteristics:
-
Malignant Tumors (Cancerous):
- Characteristics:
- Grow rapidly.
- Can invade nearby brain tissue or spread to other parts of the central nervous system (brain or spinal cord).
- Known as brain metastases when cancer spreads to the brain from other organs.
- Examples: Glioblastoma Multiforme, Astrocytomas, and Metastatic Brain Tumors.
- Characteristics:
Purpose of Brain Tumor Surgery
- Diagnostic Biopsy: To determine the type and grade of the tumor.
- Tumor Removal: To excise as much of the tumor as safely possible while preserving neurological function.
- Symptom Relief: To reduce pressure on the brain caused by the tumor.
- Improving Quality of Life: To manage symptoms like headaches, seizures, or neurological deficits.
Types of Brain Tumor Surgeries
-
Craniotomy:
- Involves removing a portion of the skull to access the tumor and then replacing the bone after surgery.
-
Endoscopic Surgery:
- Minimally invasive technique using an endoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera) to access the tumor.
-
Stereotactic Surgery:
- Uses imaging techniques (MRI or CT scans) to precisely locate the tumor for minimally invasive procedures or biopsies.
-
Laser Ablation:
- A minimally invasive procedure using lasers to destroy tumor cells.
-
Awake Brain Surgery:
- Performed while the patient is awake to monitor and preserve critical brain functions during tumor removal.
-
Shunt Placement:
- To relieve fluid build-up (hydrocephalus) often caused by tumors.
Factors Affecting Surgery
- Location: Tumors in critical areas of the brain may require specialized techniques.
- Size and Type: Larger or malignant tumors may involve more complex surgery or additional treatments like radiation or chemotherapy.
- Patient’s Health: General health and neurological condition influence the surgical approach and recover
symptoms
What do Brain Tumor surgery signs include?
Signs and Symptoms Indicating the Need for Brain Tumor Surgery
Brain tumor surgery is often recommended when a tumor in the brain causes symptoms or poses risks to the patient's health. Symptoms vary depending on the size, location, and type of tumor. Below are the key signs that may indicate the presence of a brain tumor and necessitate surgical intervention:
Common Symptoms of Brain Tumors
-
Headaches:
- Persistent or severe headaches, especially those that worsen in the morning or with activity.
- Headaches that do not respond to standard pain medications.
-
Seizures:
- Sudden, unexplained seizures, even in individuals with no prior history of epilepsy.
- Seizures may vary in type, from muscle jerking to loss of consciousness.
-
Neurological Deficits:
- Weakness or Paralysis: Difficulty moving a limb or one side of the body.
- Vision Changes: Blurred or double vision, loss of peripheral vision, or sudden blindness.
- Speech Problems: Difficulty speaking, understanding language, or slurred speech.
- Hearing Issues: Hearing loss or ringing in the ears (tinnitus).
-
Cognitive or Behavioral Changes:
- Memory problems, confusion, or difficulty concentrating.
- Changes in personality, mood swings, or unusual behavior.
-
Balance and Coordination Issues:
- Difficulty walking, maintaining balance, or performing fine motor tasks like writing.
-
Nausea and Vomiting:
- Persistent nausea or vomiting not related to other conditions, often worse in the morning.
-
Swelling or Pressure Symptoms:
- Signs of increased intracranial pressure, such as drowsiness, confusion, or unresponsiveness.
-
Fatigue:
- Constant tiredness or lack of energy unrelated to sleep or exertion.
When Surgery is Needed
Brain tumor surgery may be required if:
- The tumor is causing significant pressure on the brain.
- The tumor is located in an accessible area where it can be safely removed.
- Symptoms are severe and progressive, affecting the patient's quality of life.
- A biopsy is needed to confirm the tumor's type and grade.
- The tumor is cancerous and needs to be removed as part of comprehensive treatment.
Urgent Signs Requiring Immediate Medical Attention
- Sudden loss of consciousness.
- Rapid neurological decline (e.g., inability to speak, paralysis).
- Severe, unrelenting headaches accompanied by vomiting or confusion.
Conclusion
The symptoms associated with brain tumors often mimic those of other conditions, so an accurate diagnosis through imaging (CT scan, MRI) and evaluation by a neurologist or neurosurgeon is critical. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve outcomes and reduce complications.
risk factors
What does Brain Tumor surgery risk factor include?
Brain Tumor Surgery Risk Factors
Brain tumor surgery, while potentially life-saving, carries certain risks due to the complexity and sensitivity of operating on the brain. These risks depend on factors such as the tumor's size, location, type, and the patient’s overall health. Below are the key risk factors associated with brain tumor surgery:
General Risks of Surgery
-
Bleeding (Hemorrhage):
- Excessive bleeding can occur during or after surgery, particularly in areas with abundant blood vessels.
-
Infection:
- Infection of the incision site or within the brain (e.g., meningitis) is a potential risk.
-
Blood Clots:
- Patients may develop blood clots, such as deep vein thrombosis (DVT), during the recovery period.
Neurological Risks
-
Brain Swelling (Edema):
- Swelling around the surgical site can increase intracranial pressure and cause complications.
-
Seizures:
- Surgery may irritate brain tissue, leading to seizures post-operatively.
-
Neurological Deficits:
- Depending on the tumor's location, surgery may result in:
- Weakness or Paralysis: Especially if the tumor is near the motor cortex.
- Speech Difficulties: If the tumor is near language centers.
- Vision or Hearing Loss: If areas of the brain related to sight or hearing are affected.
- Balance or Coordination Issues: If the cerebellum is involved.
- Depending on the tumor's location, surgery may result in:
-
Cognitive Impairments:
- Memory problems, difficulty concentrating, or changes in behavior/personality can result from damage to specific brain areas.
Surgical Complications
-
Incomplete Tumor Removal:
- In some cases, the entire tumor cannot be removed due to its location near critical brain structures, leaving residual tumor tissue that may require further treatment.
-
CSF Leaks:
- Leakage of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) can occur, increasing the risk of infection.
-
Hydrocephalus:
- Accumulation of fluid in the brain may necessitate a shunt to relieve pressure.
-
Stroke:
- Damage to blood vessels during surgery can result in a stroke.
-
Coma or Death:
- Rare but severe outcomes can occur if complications arise during or after surgery.
Factors That Increase Risks
-
Tumor Location:
- Tumors near vital structures like the brainstem, optic nerve, or motor areas pose higher surgical risks.
-
Tumor Size:
- Larger tumors may require more extensive surgery, increasing the potential for complications.
-
Patient Age:
- Older patients are more vulnerable to surgical complications and slower recovery.
-
Underlying Health Conditions:
- Conditions such as diabetes, heart disease, or previous strokes can complicate surgery and recovery.
-
Malignant Tumors:
- Aggressive, fast-growing tumors may require more invasive procedures, increasing risk.
Post-Surgical Risks
-
Recurrence:
- Incomplete removal or the aggressive nature of some tumors can lead to recurrence.
-
Dependency on Rehabilitation:
- Some patients may require long-term physical, occupational, or speech therapy to regain lost functions.
-
Psychological Impact:
- Surgery and its potential effects can cause anxiety, depression, or other emotional challenges.
Minimizing Risks
- Choosing an experienced neurosurgeon and hospital with advanced technology (e.g., intraoperative MRI, neuronavigation).
- Pre-surgical evaluations and imaging to plan the safest approach.
- Post-operative monitoring in an ICU setting for early detection of complications.
- Rehabilitation and regular follow-ups to address any deficits or residual issues.
Conclusion
Brain tumor surgery in India involves inherent risks, but advancements in neurosurgical techniques and technologies have significantly improved safety and outcomes. Understanding these risks and working closely with a skilled medical team helps ensure the best possible results.
preparation
How do you prepare for brain tumor surgery?
Preparing for brain tumor surgery involves both medical and practical steps to ensure the procedure is as safe and effective as possible. Below is a detailed guide on how to prepare:
1. Choose the Best Option for Surgery
- Research and select a highly experienced neurosurgeon and a reputable hospital in your city or abroad.
- Consider factors like hospital accreditation, surgeon experience, success rates, and patient testimonials.
- Discuss your specific condition and surgical options with your doctor.
2. Pre-Surgery Check-Up (PSC)
- Diagnostic Tests:
- Blood Tests: To check for infections, clotting ability, and overall health.
- ECG (Electrocardiogram) and ECHO: To ensure the heart is healthy enough for surgery.
- Urine Tests: To rule out infections or abnormalities.
- Imaging Studies: MRI or CT scans to map the tumor and plan the surgical approach.
- Assessment:
- The results will determine if you are fit for surgery.
3. Pre-Surgical Instructions
-
Consent Form:
- You’ll be required to sign a consent form giving the surgeon permission to perform the surgery.
-
Medication Review:
- Inform your doctor about all medications, including over-the-counter drugs, supplements, and herbal remedies.
- Stop blood thinners (e.g., aspirin, warfarin, clopidogrel) at least 7–10 days before surgery to reduce the risk of excessive bleeding.
-
Fasting:
- You will be advised to avoid food and drinks (fasting) for 8–12 hours before the procedure.
4. Lifestyle Adjustments Before Surgery
- Quit Smoking and Alcohol:
- These can affect healing and anesthesia safety.
- Healthy Diet:
- Eat a nutritious diet leading up to surgery to boost immunity and recovery.
5. Admission to the Hospital
- You will typically be admitted on the day of the procedure or the day before.
- The medical team will review your test results and provide final instructions.
6. Mental and Emotional Preparation
- Discuss any concerns or questions with your doctor.
- Engage in relaxation techniques like meditation to ease anxiety.
- Speak with a counselor, if needed, to address emotional concerns.
Cost of Brain Tumor Surgery in India
- Estimated Cost: $5,000 to $7,000 USD.
- This can vary based on factors such as:
- Surgeon’s Experience
- Hospital Facilities
- City (Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, Chennai, etc.)
- Patient’s Condition and complexity of the procedure.
- This can vary based on factors such as:
Why Choose India for Brain Tumor Surgery?
- Affordable Cost compared to Western countries.
- Availability of world-class hospitals with advanced facilities.
- Highly skilled and experienced neurosurgeons.
- Excellent patient care and recovery support.
Top Tips
- Follow all pre-surgical instructions provided by your healthcare team.
- Arrange for a trusted family member or friend to accompany you and assist during recovery.
- Discuss post-surgery recovery plans, including rehabilitation, with your doctor in advance.
Proper preparation for brain tumor surgery in India is essential for the best surgical outcomes and a smoother recovery process.
procedure
How is the Brain Tumour Surgery Procedure done?
Brain Tumor Surgery and Treatment Procedures
Brain tumor treatment depends on the type, size, and location of the tumor as well as the patient’s overall health. Below is a detailed explanation of the procedures and techniques used for brain tumor surgery and related treatments:
1. Brain Tumor Surgery
The primary method for treating brain tumors is surgical removal.
Procedure:
-
Incision:
- A neurosurgeon makes an incision in the scalp and removes a section of the skull (craniotomy) to access the brain.
-
Tumor Removal:
- Using advanced imaging techniques (e.g., intraoperative MRI or CT scans), the surgeon locates the tumor.
- Depending on its location, part or all of the tumor is removed:
- Complete Resection: When the tumor is in an accessible area and can be fully removed.
- Partial Resection: If the tumor is near vital brain structures, only a portion may be safely removed.
-
Closing:
- After the tumor removal, the skull section is replaced, and the incision is closed with sutures or staples.
Goals:
- Relieve symptoms caused by the tumor (e.g., headaches, seizures).
- Reduce pressure in the brain.
- Remove as much of the tumor as possible without causing damage to healthy brain tissue.
2. Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to destroy cancer cells and shrink tumors.
Procedure:
- External Beam Radiation:
- Delivered over multiple sessions using focused radiation beams.
- Used to treat residual tumor cells after surgery.
- Benefits:
- Controls tumor growth and prevents recurrence.
- Especially useful for inoperable tumors or cancer that has spread (metastasized).
3. Radiosurgery
Radiosurgery is a non-invasive treatment that uses targeted radiation to treat small tumors or lesions.
Types:
- Gamma Knife Surgery:
- Delivers highly focused gamma rays to a specific area of the brain.
- Ideal for small tumors or lesions near critical structures.
- Stereotactic Radiosurgery:
- Uses advanced imaging and computer technology to precisely deliver radiation.
- Minimizes damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Procedure:
- Performed as an outpatient (daycare) procedure.
- Does not involve surgical incisions.
- Patients can return to normal activities quickly.
4. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves using drugs to destroy or control the growth of cancer cells.
Procedure:
- Administered orally, intravenously, or through wafers placed directly in the brain during surgery.
- Often combined with surgery and radiation therapy to improve outcomes.
Goals:
- Shrink tumors before surgery.
- Eliminate residual cancer cells post-surgery.
- Prevent tumor recurrence.
5. Targeted Drug Therapy
This treatment focuses on specific molecular changes in cancer cells to stop their growth.
Common Drugs:
- Bevacizumab (Avastin):
- Inhibits blood vessel formation in tumors, cutting off their nutrient supply.
- Everolimus (Afinitor):
- Targets specific proteins involved in tumor growth.
Role:
- Often used for recurrent tumors or when standard therapies are ineffective.
- Typically a supplementary treatment rather than a primary one.
Considerations for Choosing a Treatment Plan
- Tumor Type:
- Benign or malignant.
- Primary or metastatic.
- Tumor Location:
- Accessibility and proximity to vital brain structures.
- Patient Condition:
- Age, overall health, and tolerance to treatments.
- Goals of Treatment:
- Symptom relief, life extension, or improving quality of life.
Conclusion
Brain tumor treatment often involves a combination of surgery, radiation, and chemotherapy. Emerging technologies like radiosurgery and targeted therapies further improve outcomes, especially for complex or advanced cases. Choosing the right treatment plan requires collaboration with a skilled neurosurgeon and a multidisciplinary medical team.
post procedure
What is the Brain Tumour Post Surgery Care?
Post-Surgery Care for Brain Tumor Patients
Proper care following brain tumor surgery is essential for recovery and minimizing complications. Below is a detailed guide on post-operative care:
1. Hospital Stay and Immediate Recovery
-
Monitoring:
- After surgery, patients are kept in the intensive care unit (ICU) for close monitoring of vital signs and neurological function.
- The medical team observes for any signs of complications, such as swelling, bleeding, or infection.
-
Pain Management:
- Medications will be prescribed to manage pain and discomfort.
- Anti-seizure medications may also be given to prevent seizures.
-
Initial Mobilization:
- Patients are encouraged to move around gently as soon as it is safe to prevent blood clots and promote circulation.
2. Care of Incisions
- Cleaning and Dressing:
- The surgical site must be kept clean and dry.
- Dressings should be changed as per the surgeon's instructions.
- Stitches or Staples:
- Stitches or staples are typically removed 7 to 10 days after surgery during a follow-up visit.
- Signs of Infection:
- Monitor the incision for redness, swelling, or discharge.
- Report any fever or unusual symptoms to the doctor immediately.
3. Medications
- Pain Relievers: To control postoperative pain.
- Antibiotics: To prevent infection.
- Anti-Seizure Medications: Often prescribed, especially if the patient had seizures before surgery or the tumor affected brain areas linked to seizures.
- Steroids: To reduce brain swelling and inflammation.
4. Physical and Neurological Recovery
-
Physical Therapy:
- Helps patients regain strength, balance, and mobility.
-
Occupational Therapy:
- Aids in adapting to daily tasks and routines if motor or cognitive functions are affected.
-
Speech Therapy:
- Recommended for patients with difficulty speaking or swallowing due to surgery.
-
Cognitive Rehabilitation:
- Focuses on improving memory, attention, and problem-solving skills.
5. Activity Restrictions
-
Avoid Heavy Lifting:
- Refrain from strenuous activities, heavy lifting, or intense physical exertion for several weeks.
-
Driving:
- Driving is not recommended until cleared by the surgeon, especially for those on anti-seizure medications.
-
Rest and Sleep:
- Ensure adequate rest to aid healing, but gradually increase activity levels as advised by the doctor.
6. Follow-Up Appointments
- Regular follow-ups with the neurosurgeon to monitor healing and discuss any concerns.
- Additional MRI or CT scans may be done to ensure no tumor remnants remain and to assess recovery.
7. Lifestyle Adjustments
- Diet:
- Follow a balanced, nutritious diet to promote healing and strengthen the immune system.
- Hydration:
- Drink plenty of fluids unless otherwise restricted by the doctor.
- Smoking and Alcohol:
- Avoid smoking and alcohol as they can interfere with healing.
8. Emotional and Psychological Support
- Emotional Well-Being:
- Surgery and recovery can be emotionally taxing. Counseling or therapy can help manage stress and anxiety.
- Support Groups:
- Joining a support group for brain tumor survivors can provide emotional encouragement and shared experiences.
9. Potential Signs to Watch for Post-Surgery
Seek immediate medical attention if you experience:
- Severe headaches or sudden changes in mental status.
- Persistent nausea or vomiting.
- Weakness or loss of sensation in any part of the body.
- Difficulty speaking, seeing, or swallowing.
- Seizures.
- Signs of infection (fever, redness, swelling, or discharge from the incision).
10. Long-Term Care
- Depending on the tumor type, additional treatments like radiation or chemotherapy may be necessary.
- Lifelong monitoring may be required to check for tumor recurrence or long-term effects of the surgery.
Proper adherence to post-surgery care instructions significantly impacts recovery outcomes and quality of life. Always maintain open communication with your medical team for the best guidance.
success rate
What is the Brain Tumour Surgery Success Rate?
Brain Tumor Surgery Success Rate
The success of brain tumor surgery depends on several factors, including the type, size, location, and stage of the tumor, as well as the patient’s overall health and age. Here’s a breakdown of the key factors and outcomes:
1. Success Rate Overview
-
Benign Tumors (Non-Cancerous):
- Surgery for benign tumors has a high success rate, often exceeding 90% when the tumor is accessible and completely removed.
- Patients generally experience full recovery, especially if the tumor has not caused significant neurological damage.
-
Malignant Tumors (Cancerous):
- The success rate varies depending on the type and grade of the tumor.
- For low-grade gliomas, the survival rate is relatively high, with many patients living beyond 5 years.
- High-grade gliomas, such as glioblastomas, are more challenging to treat. Surgery can help alleviate symptoms and prolong survival but is rarely curative.
2. Factors Influencing Success
-
Tumor Accessibility:
- Tumors in areas of the brain that are easily reachable and not near critical structures have higher removal success rates.
- Deep-seated or complex tumors near vital regions may require partial removal to avoid complications.
-
Complete vs. Partial Resection:
- Complete removal often leads to better outcomes and lower recurrence rates.
- Partial removal may require additional treatments, such as radiation or chemotherapy.
-
Patient Health:
- Younger patients and those with no significant comorbidities tend to recover more successfully.
-
Advanced Techniques:
- Use of technologies like intraoperative MRI, neuronavigation, and awake brain surgery significantly increases precision and reduces risks.
3. Additional Treatment Contributions
-
Radiation Therapy:
- Enhances outcomes by targeting residual tumor cells and reducing recurrence risks.
-
Chemotherapy:
- Can prolong survival for certain types of malignant tumors when combined with surgery and radiation.
-
Emerging Therapies:
- Targeted drug therapies and immunotherapies continue to improve the prognosis for patients with specific genetic mutations.
4. Long-Term Outcomes
-
Recurrence:
- Benign tumors, if fully removed, rarely recur.
- Malignant tumors often require lifelong monitoring and ongoing treatments to manage recurrence risks.
-
Quality of Life:
- Many patients experience significant improvement in symptoms such as headaches, seizures, and neurological deficits post-surgery.
5. Estimated Survival Rates
-
Benign Tumors:
- 10-year survival rates are very high, often exceeding 95% with early intervention.
-
Low-Grade Malignant Tumors:
- 5-year survival rates range from 70% to 90%, depending on tumor type and treatment.
-
High-Grade Malignant Tumors:
- Glioblastoma: Median survival is 12–18 months, with a small percentage living beyond 5 years when treated with surgery and adjuvant therapies.
Conclusion
Brain tumor surgery has a high success rate, particularly for benign and early-stage tumors. While malignant tumors present greater challenges, advancements in surgical techniques and supplementary treatments continue to improve outcomes and survival rates. Early diagnosis and treatment remain critical for the best results.
faqs from doctor
What questions should I ask about a brain tumor?
Answers to Your Brain Tumor Questions
-
Are you a board-certified top neurosurgeon in India?
Yes, always confirm that your neurosurgeon is board-certified and has extensive experience in brain tumor surgeries. You can also inquire about their specialization in specific types of tumors or advanced surgical techniques, and are you Top 10 Neurosurgeon in India -
How many years of experience do you have in this field?
Most top neurosurgeons in India have 15–30 years of experience. Ensure your surgeon has significant expertise in handling complex brain tumor cases. -
Do you have the top 10 brain tumor treatment centers in India?
The leading brain tumor treatment centers in India include AIIMS (Delhi), Apollo Hospitals, Fortis Hospitals, Medanta, and others. A reputable surgeon will typically have affiliations with one or more of these centers. -
How many surgeries are you doing every day for brain tumor surgery?
A highly experienced neurosurgeon may perform 2–3 brain tumor surgeries weekly, depending on the complexity of the cases and the available infrastructure. -
How much does brain tumor surgery cost in India?
The cost ranges from ₹2,00,000 to ₹7,00,000 ($2,500–$9,000), depending on the hospital, surgeon’s expertise, and the complexity of the surgery. -
In India, what is the cost of radiation therapy for brain tumors?
Radiation therapy costs between ₹1,50,000 and ₹3,00,000 ($2,000–$4,000), depending on the type of radiation (e.g., IMRT, CyberKnife, or Proton Therapy). -
Am I a good patient for you for brain tumor surgery?
This depends on factors like tumor type, location, size, your overall health, and prior treatments. Your surgeon will assess these through imaging and medical evaluations. -
What type of brain tumor do I have?
The tumor type is determined through imaging (MRI/CT scans) and biopsy. Common types include gliomas, meningiomas, pituitary tumors, and metastatic brain tumors. -
Let me know the success rates and how long time will take for recovery.
Success rates vary but are generally high for benign tumors (90–95%). Recovery time ranges from 4–8 weeks, depending on the complexity of the surgery and individual health. -
What treatment plan do you recommend and why?
The treatment may involve surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or a combination. The plan depends on the tumor type, grade, location, and overall health. -
What are the advantages and disadvantages of brain tumor surgery?
Advantages: Removal or reduction of the tumor, symptom relief, and potential cure for benign tumors.
Disadvantages: Risks include infection, bleeding, neurological deficits, or recurrence of the tumor. -
How long do I have to stay in and outside the hospital?
Hospital stay is typically 5–7 days, with additional recovery at home for 4–6 weeks. Rehabilitation may be needed in some cases. -
What are the risk factors for this type of surgery?
Risks include infection, blood clots, swelling, seizures, and changes in neurological function like speech or movement. -
When can I go for normal activities, including exercise?
Light activities can resume in 4–6 weeks, but heavy exercise, depending on recovery progress, may require 3–6 months. -
Do I have stitches, staples, and bandages?
Yes, most surgeries involve stitches or staples to close the incision. These are typically removed 10–14 days after surgery. -
Do I need to go for another surgery in the future?
This depends on the tumor type. For benign tumors, additional surgery is rare unless there is a recurrence. Malignant tumors may require further interventions. -
May I know the top 10 brain tumor treatment centers in India?
- ARTEMIS HOSPITAL
- MANIPAL HOSPITAL
- BLK HOSPITAL
- APOLLO HOSPITAL
- FORTIS HOSPITAL
- MAX HOSPITAL
- MEDANTA HOSPITAL
- YASHODHA HOSPITAL
- GLOBAL HOSPITAL
- NARAYANA HOSPITAL
-
Do I need any follow-up appointments or tests after my surgery?
Yes, regular follow-ups and imaging (MRI or CT) are essential to monitor recovery and check for recurrence. These are typically scheduled every 3–6 months initially, then annually.




























